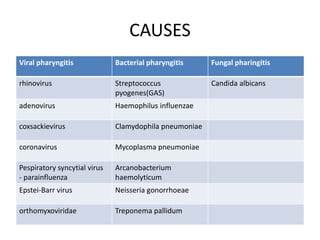
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the throat characterized by pain, irritation, and difficulty swallowing, with common causes including viral and bacterial infections. Transmission occurs primarily through respiratory droplets and direct contact with secretions, and prevention involves good hygiene practices. Diagnosis includes symptom assessment and testing for bacteria, while treatment varies between viral infections that typically resolve on their own and bacterial infections that require antibiotics.