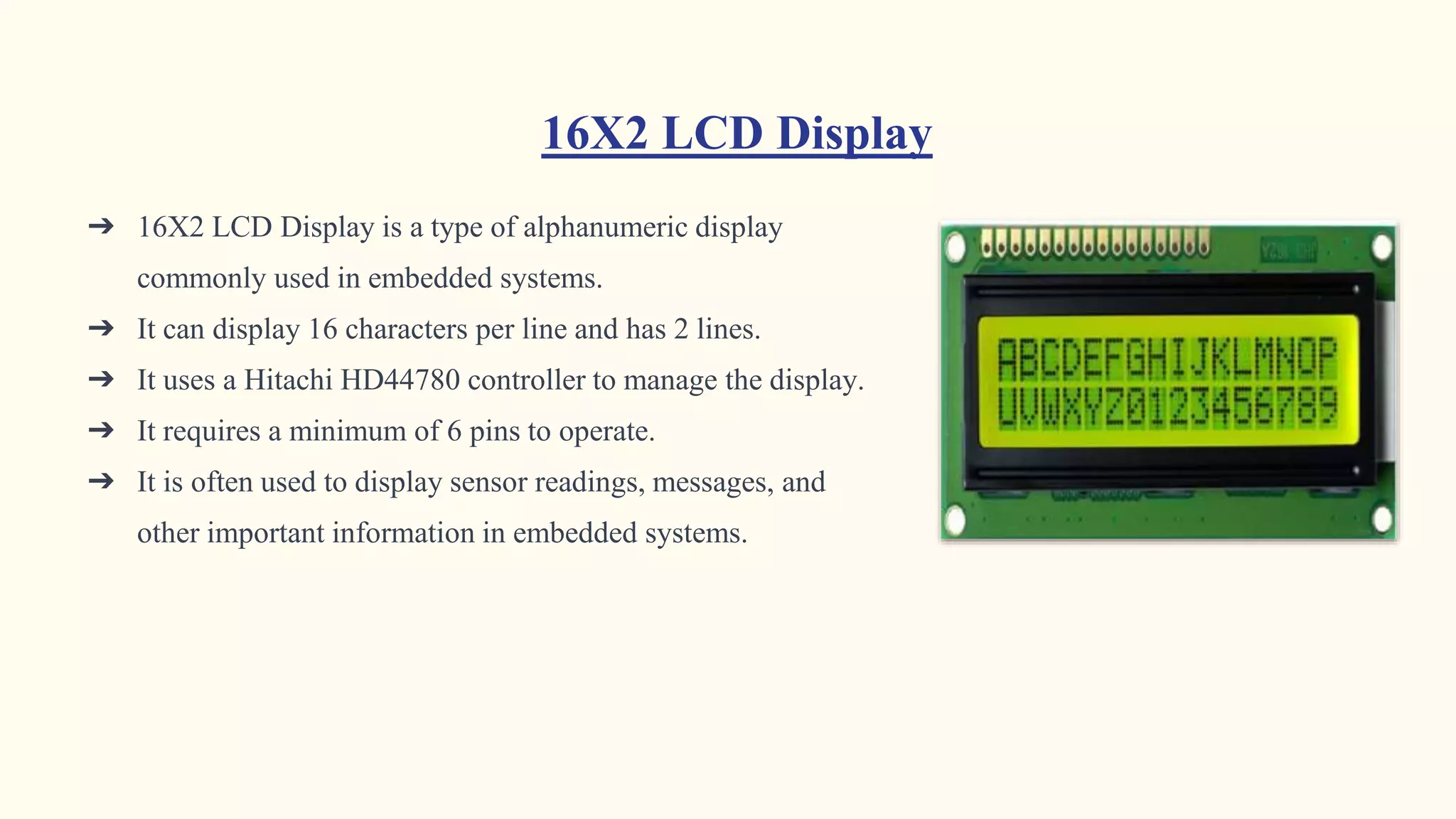
This document describes an IoT-based garbage monitoring system project. The system uses ultrasonic sensors placed in garbage bins to detect waste levels. Sensor data is transmitted to a server via NodeMCU ESP8266 WiFi modules. The server analyzes the data to optimize garbage collection routes and schedules. The system aims to improve waste management efficiency by only collecting bins when full. It faces challenges regarding implementation costs and potential technical issues. Overall, the IoT-based approach provides a promising solution for more sustainable waste management.