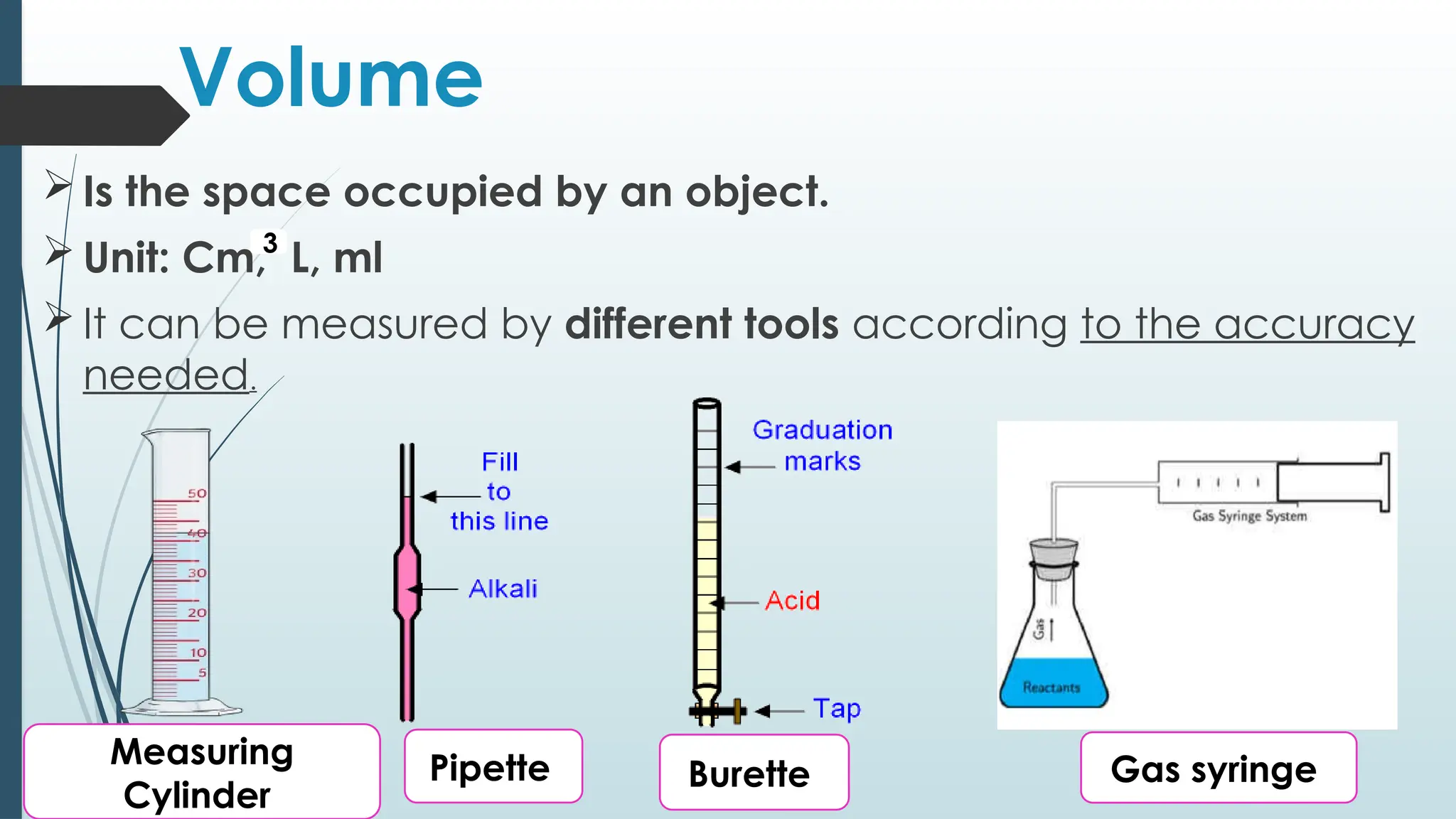
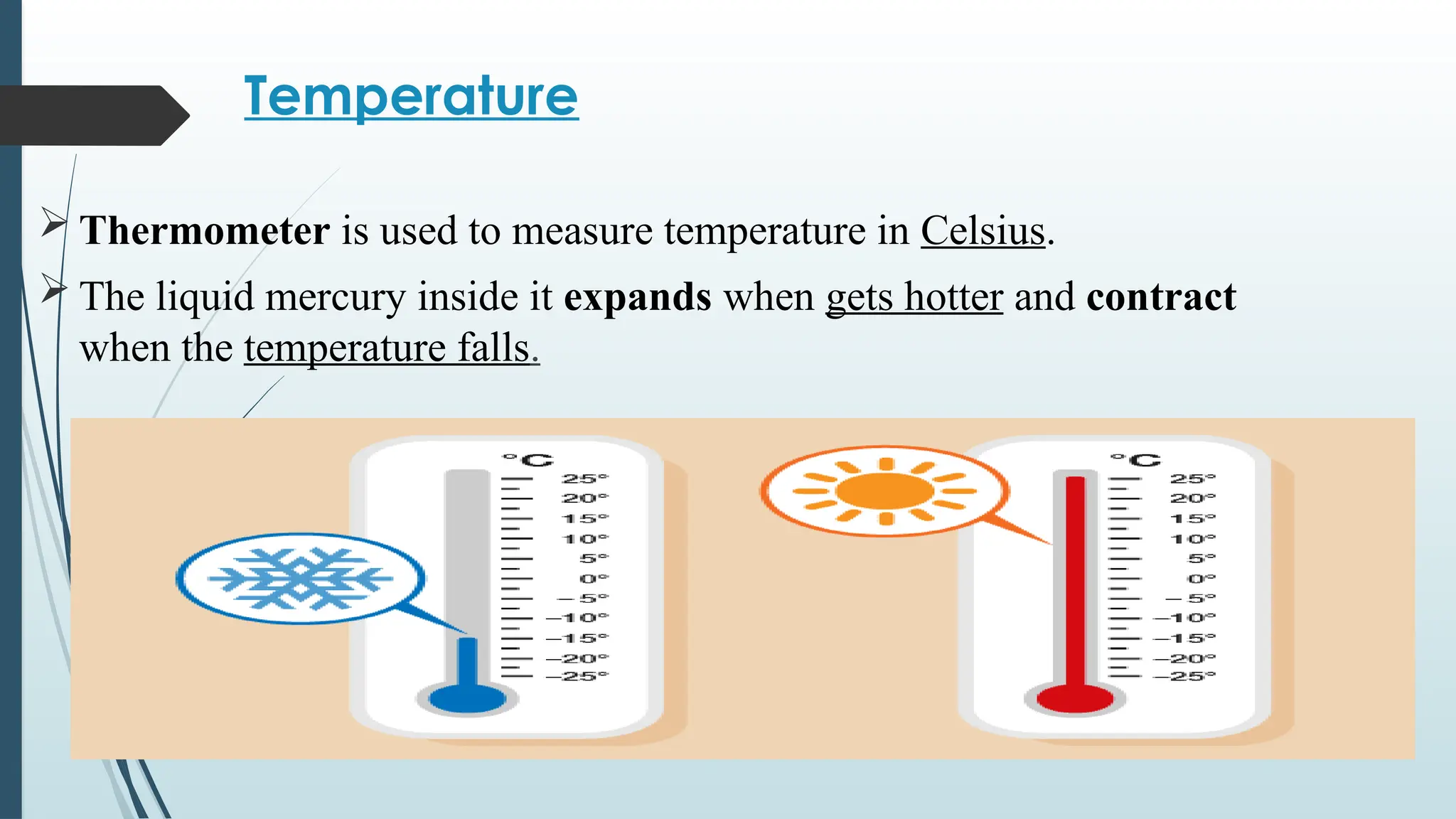
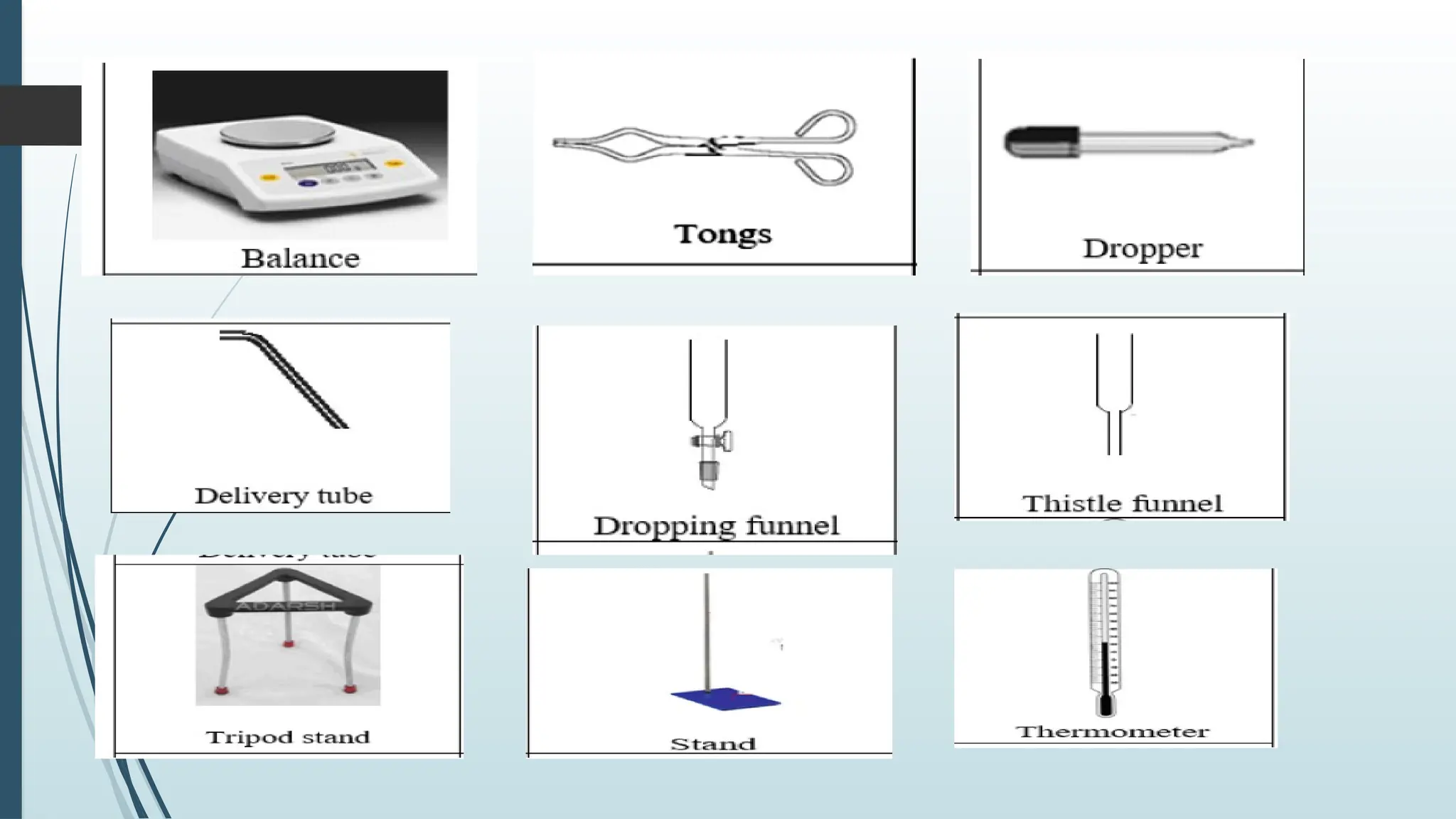
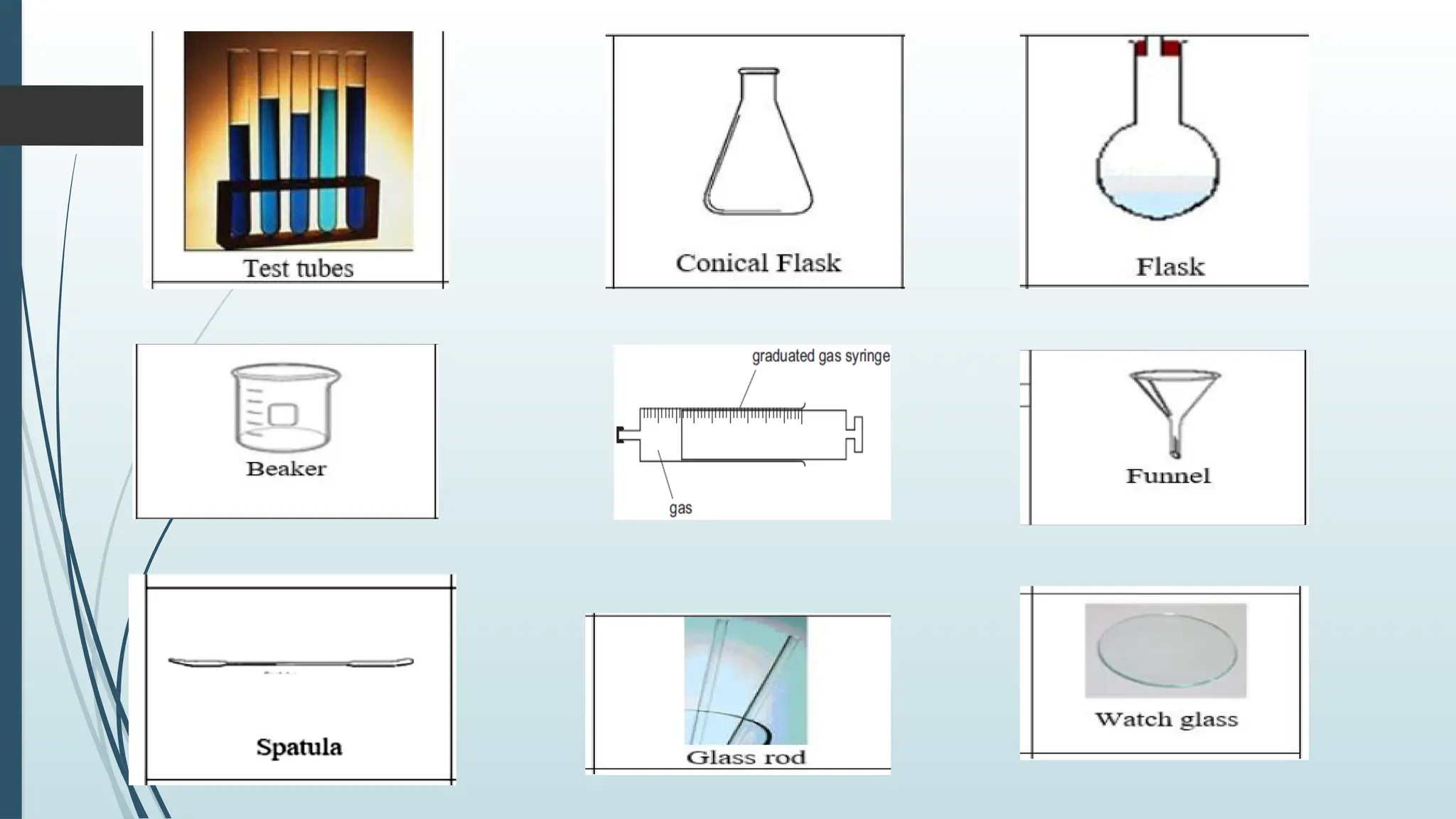
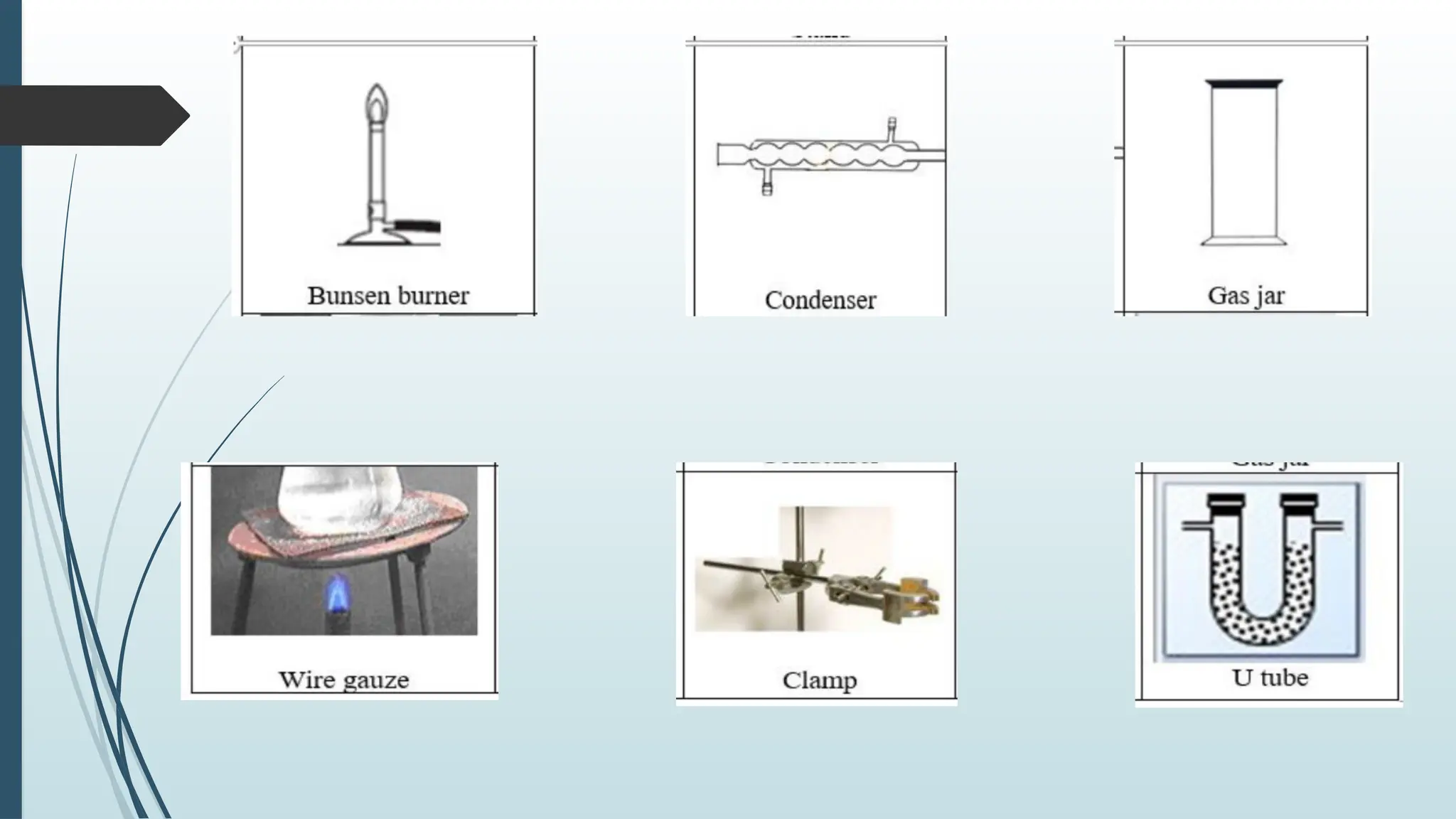
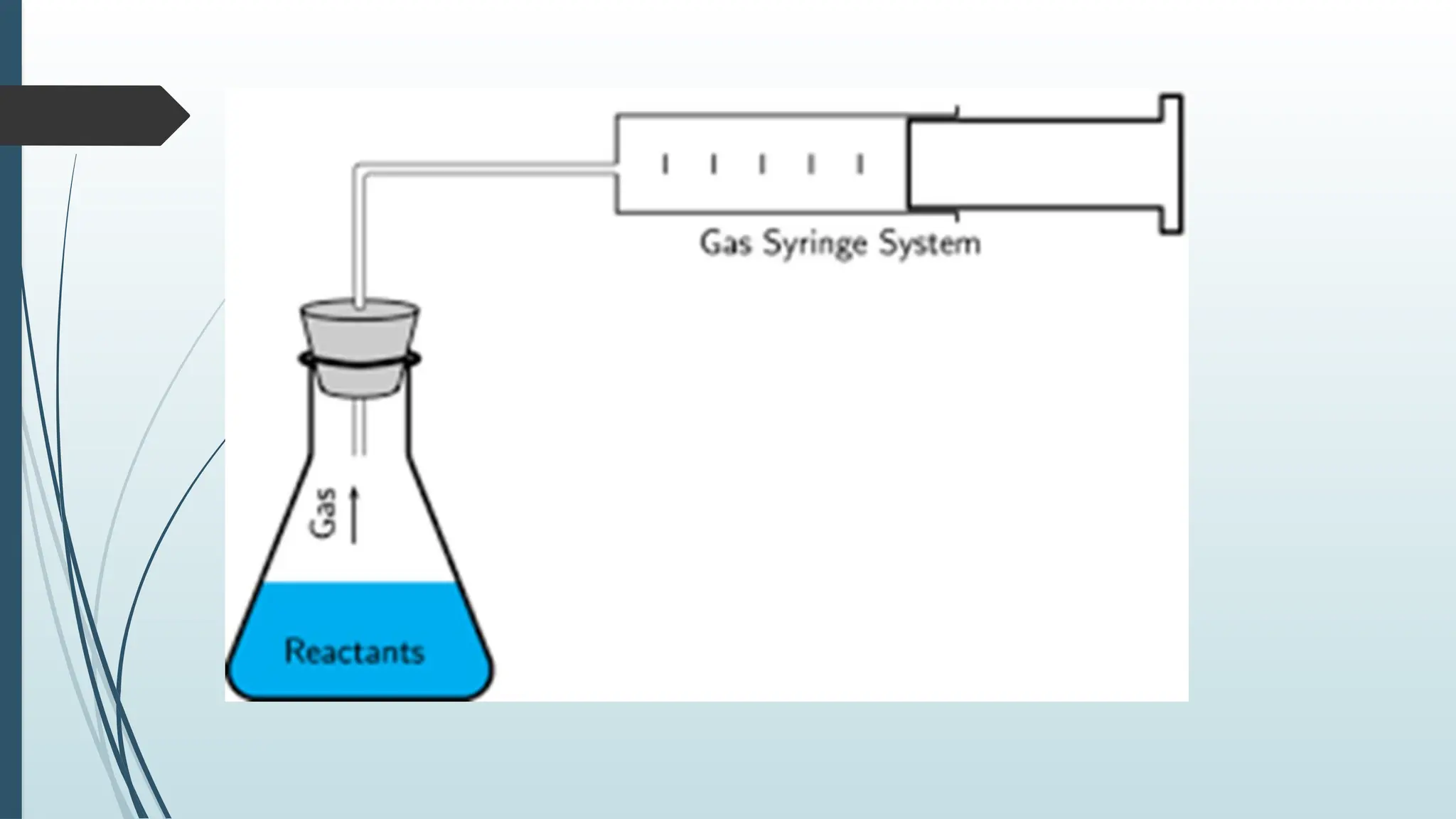
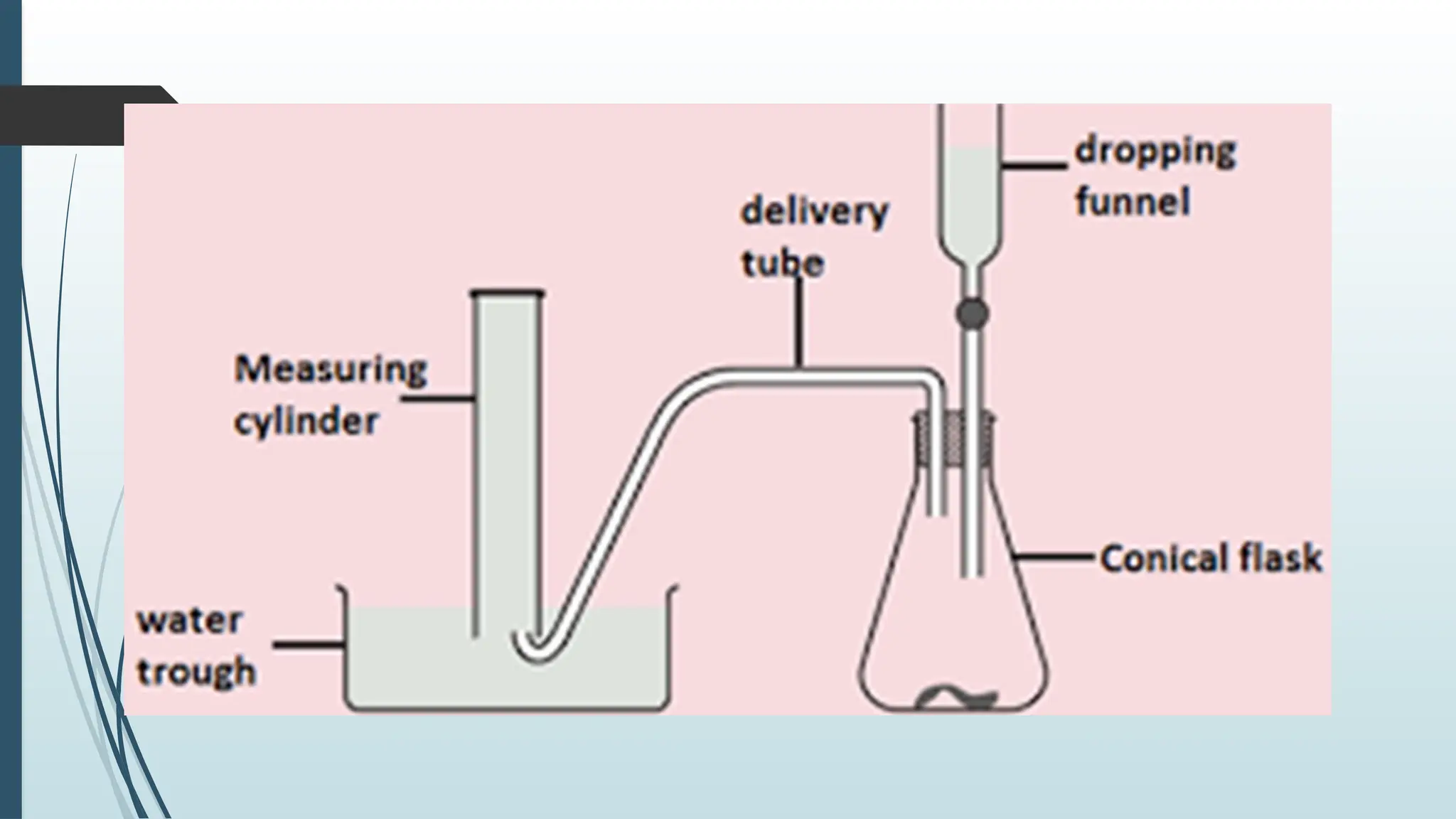
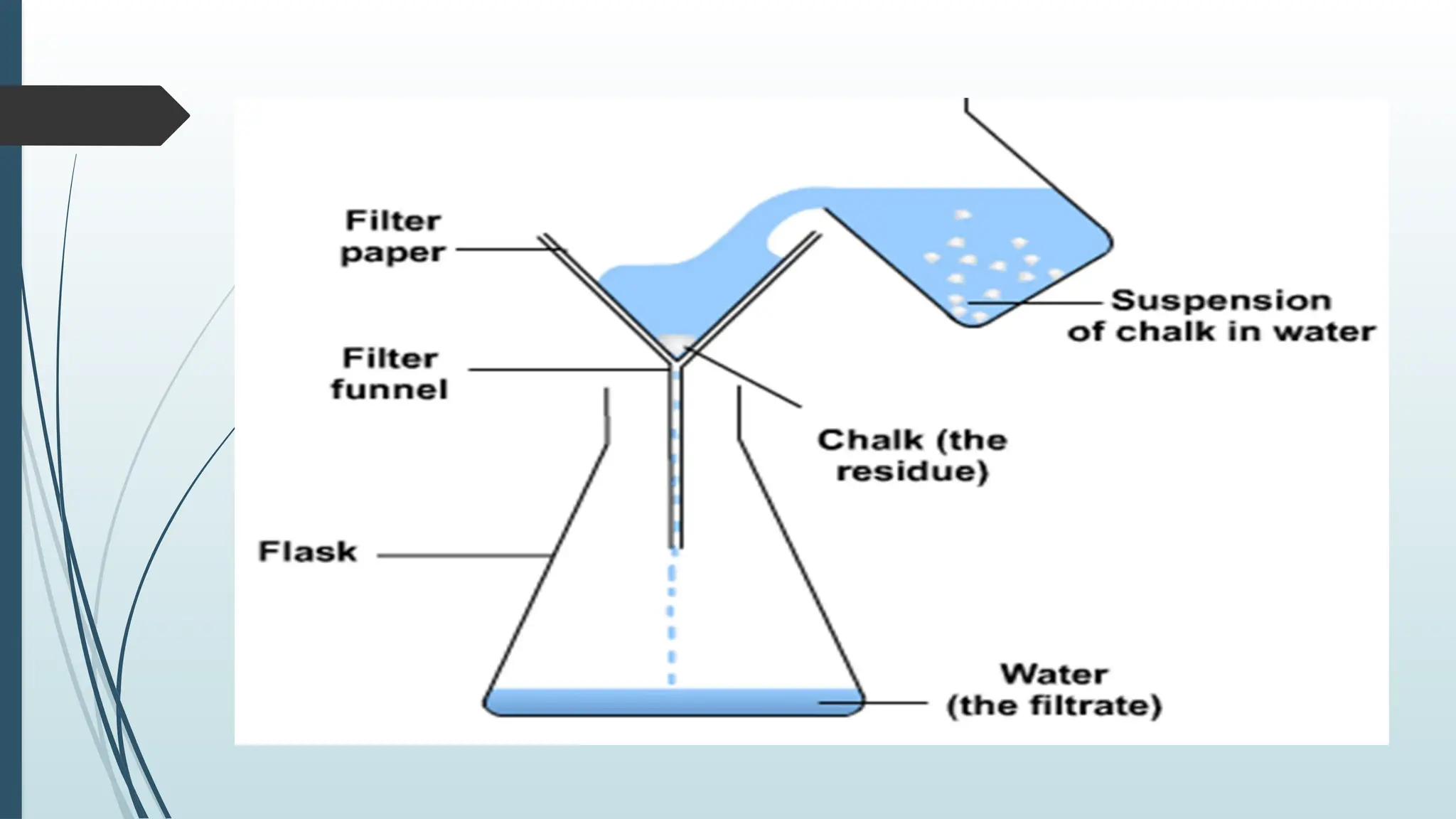
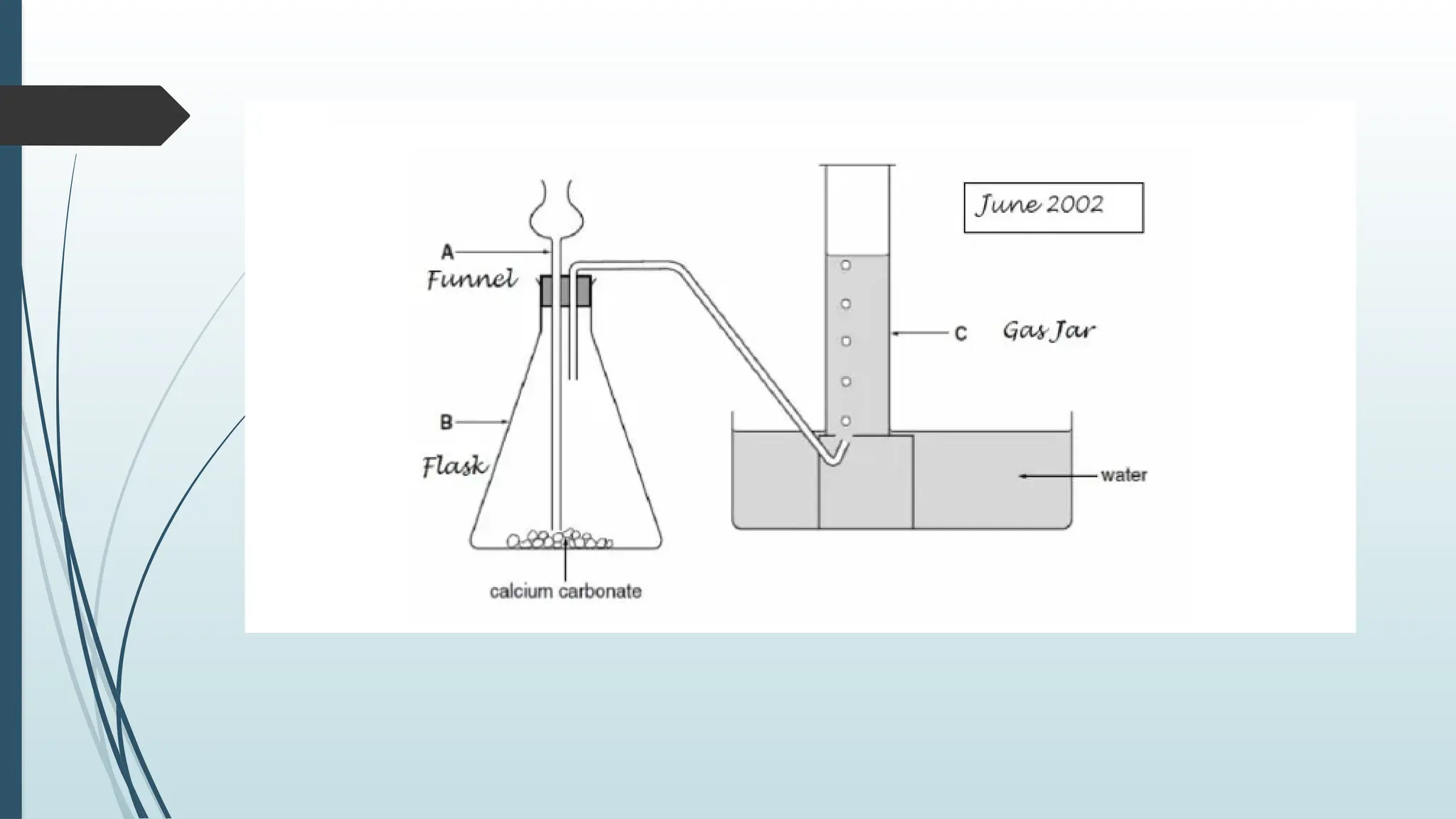
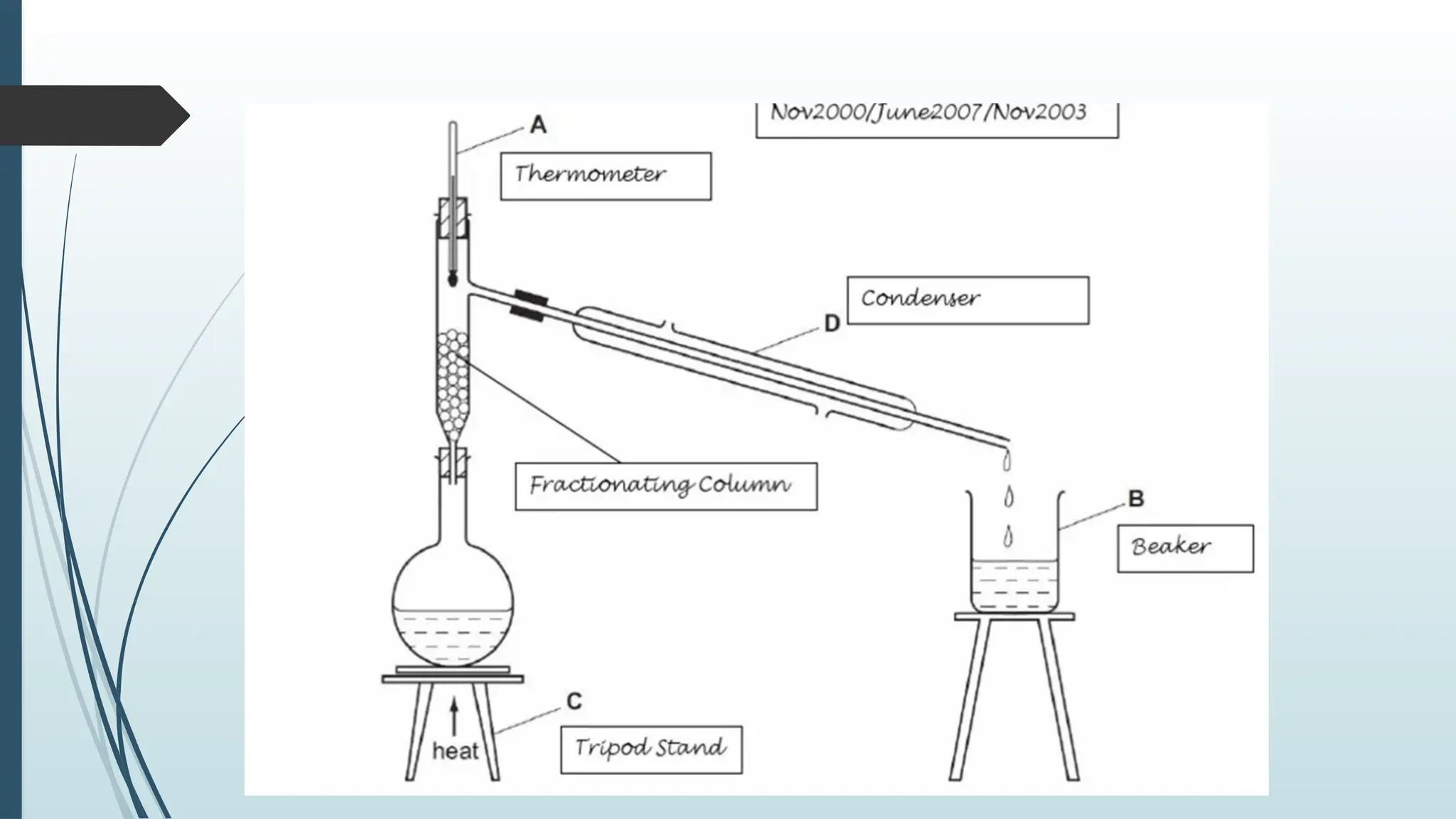
The document details fundamental measurements in a laboratory, including mass, volume, temperature, and time, along with respective units and measuring tools. It emphasizes laboratory safety rules such as proper attire, handling chemicals, and disposal of waste. Additionally, it highlights the importance of following instructions and recognizing hazard symbols to ensure a safe working environment.