The document discusses various topics related to measurement in physics, including:
- The need for measurement during experiments to understand physical phenomena and compare quantities.
- Common physical quantities like mass, length, time, temperature and pressure that are measured.
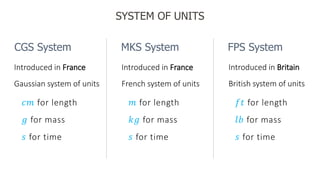
- Types of physical quantities as fundamental or derived and units used for measurement like meters, kilograms, seconds.
- International System of Units (SI) which standardizes units for scientific work.
- Scientific notation used to conveniently write very large and small numbers.
- Conversion factors and examples of converting between different units.
- Order of magnitude as a way to approximate the comparison between very large and small quantities.