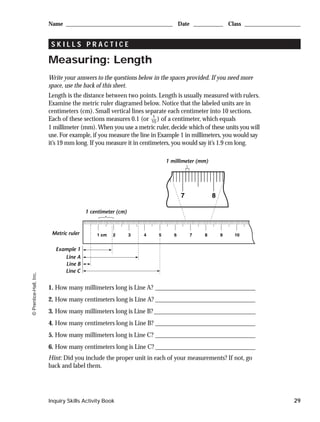
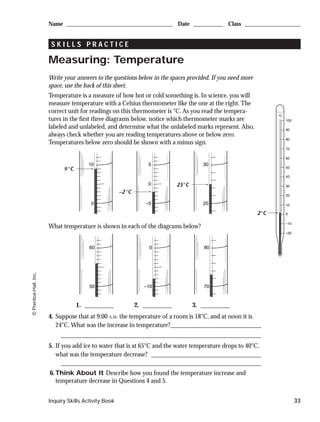
1. The document provides instructions on measuring various quantities like length, volume, mass, and temperature using standard metric units.
2. It describes the International System of Units (SI) and common prefixes used for naming smaller and larger metric units.
3. Tips are given for properly making measurements, including knowing the purpose and tools, labeling results, and following special rules for different instruments.