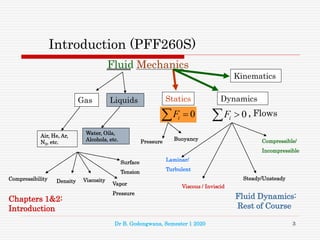
This document introduces a course on Process Fluid Flow. It will cover topics including the definitions and properties of fluids, fluid statics, the Bernoulli and energy equations, flow in pipes and piping systems. Students will study gases, liquids and fluid dynamics, as well as fluid flow applications in fields like oceanography, meteorology, biomedical engineering and aeronautics. The course aims to provide models and equations to predict and analyze fluid motion and behavior.