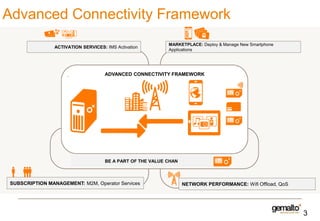
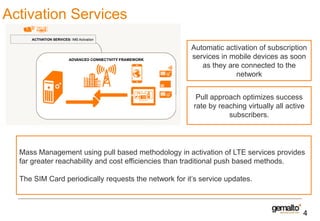
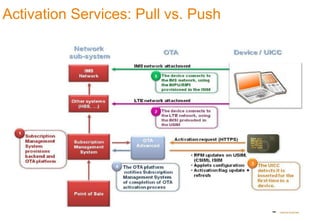
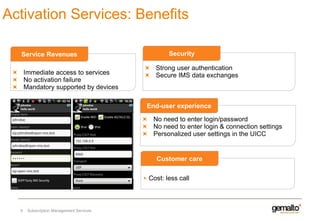
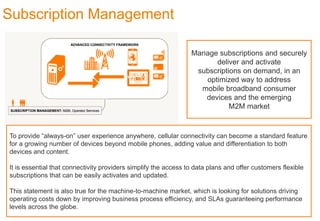
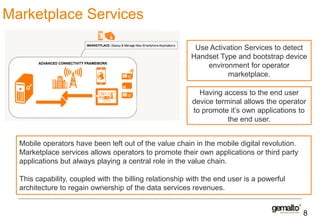
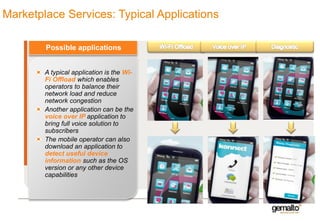
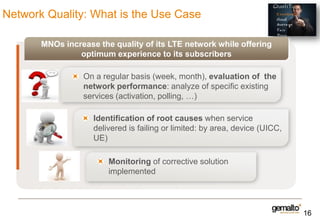
This document discusses various services that mobile network operators can provide using an advanced connectivity framework in the LTE world. It summarizes services for activation, subscription management, marketplace services, and network quality monitoring. Activation services allow automatic activation of subscriptions using a pull-based methodology for greater reach and efficiency. Subscription management provides flexible subscriptions that can be easily activated and updated. Marketplace services allow operators to promote their own applications and play a central role in the value chain. Network quality monitoring provides insights into network performance from aggregated subscriber data.