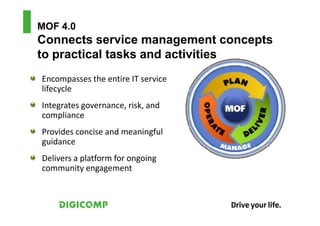
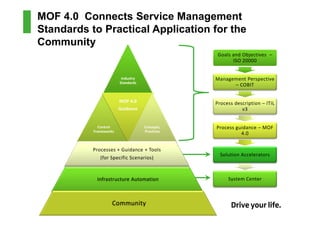
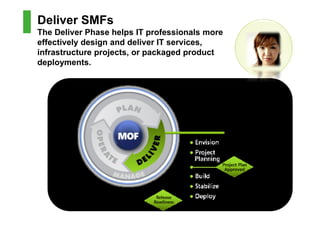
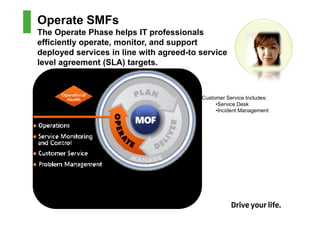
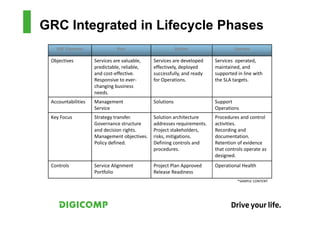
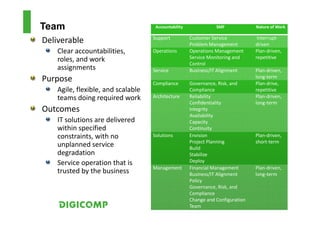
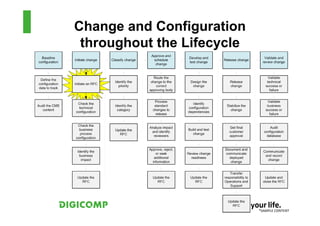
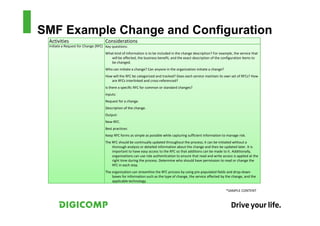
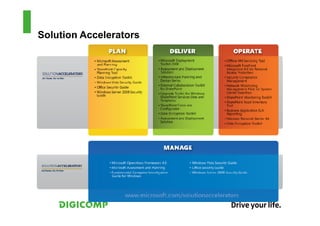
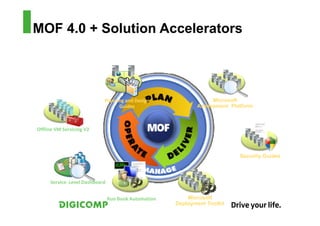
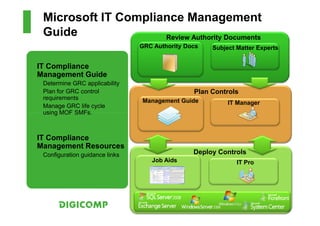
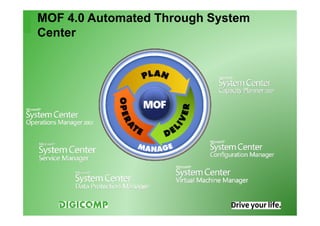
This document provides an introduction to the Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF). It discusses how MOF connects service management concepts to practical tasks and activities. MOF encompasses the entire IT service lifecycle and integrates governance, risk, and compliance. It provides concise guidance and delivers a platform for ongoing community engagement to help IT organizations efficiently and effectively deliver IT services. The document then provides examples of how MOF can be applied through its phases, service management functions, and use of solution accelerators.