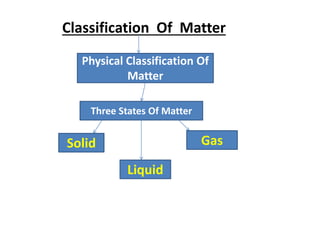
This document discusses the classification of matter. It defines matter as substances that have mass and volume and occupy space. Matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms and molecules. The characteristics of these particles determine the three states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape and volume, do not flow, and are rigid and incompressible. Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container, and can flow and diffuse. Gases have no definite shape or volume, and will expand to fill their container. Non-matter substances have no mass or volume and are examples of energy or abstract concepts.