Recommended
PPTX
Circles and it's Arc MATHEMATICS 10.pptx
PDF
introduction to circle geometry - grade 10 mathematics 1
PPTX
Terms and Definitions related to circle.pptx
PPTX
knowing what is CIRCLE AND ITS CORRESPONDING PARTS
PPTX
CIRCLE MAE0 142 joyce.pptx
PPTX
L1.Chord,Arc,Central and Inscribed Angle.pptx
PPTX
ARCS and chords.pptx Mathematics garde 10 lesson about circles. This is the ...
PPTX
4 - Circle and It's Parts. 4 - Circle and It's Parts.pptx
PPT
powerpoint presentation for introduction of the circle
PPTX
circleanditsparts-130904032217--converted.pptx
PPTX
Lesson 6 - Circle basic concepts of circle
PPTX
Grade 10_Math-Chapter 3_Lesson 3-1 Central Angles and Inscribed Angles a.pptx
PPT
PPTX
Mathematics 10 The Relations among Chords, Arcs,.pptx
PPTX
circles.pptx circles.pptx circles.pptx circles.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
G10 Math Q2- Week 2_3 Proves Angles Arcs.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
CIRCLE geometry lesson 2nd quarter grade 10
PPTX
CIRCLES and its parts: Tangent, secant ,radius, diameterptx
PDF
PPT
Second Quarter Topic _Arcs and Central A
PPT
Basic termscircles-1193893440612337-2
PPTX
this PowerPoint presentation is all about circles
PPTX
Arcs and angles of circles
PPTX
Presentation on the topic of mathematics - Circle
PPTX
Circle Presentation on a topic in mathematics.pptx
PDF
Grade 9 (Alternate) Mathematics III - Learning Modules for EASE Program of DepEd
PPTX
Simulation Learning in Health Sciences and Human Service programs at Camosun ...
PPTX
How to perform product search based on a custom field from the Website Shop p...
More Related Content
PPTX
Circles and it's Arc MATHEMATICS 10.pptx
PDF
introduction to circle geometry - grade 10 mathematics 1
PPTX
Terms and Definitions related to circle.pptx
PPTX
knowing what is CIRCLE AND ITS CORRESPONDING PARTS
PPTX
CIRCLE MAE0 142 joyce.pptx
PPTX
L1.Chord,Arc,Central and Inscribed Angle.pptx
PPTX
ARCS and chords.pptx Mathematics garde 10 lesson about circles. This is the ...
PPTX
4 - Circle and It's Parts. 4 - Circle and It's Parts.pptx
Similar to Mathematics CHORDS, ARCS AND ANGLES.pptx
PPT
powerpoint presentation for introduction of the circle
PPTX
circleanditsparts-130904032217--converted.pptx
PPTX
Lesson 6 - Circle basic concepts of circle
PPTX
Grade 10_Math-Chapter 3_Lesson 3-1 Central Angles and Inscribed Angles a.pptx
PPT
PPTX
Mathematics 10 The Relations among Chords, Arcs,.pptx
PPTX
circles.pptx circles.pptx circles.pptx circles.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
G10 Math Q2- Week 2_3 Proves Angles Arcs.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
CIRCLE geometry lesson 2nd quarter grade 10
PPTX
CIRCLES and its parts: Tangent, secant ,radius, diameterptx
PDF
PPT
Second Quarter Topic _Arcs and Central A
PPT
Basic termscircles-1193893440612337-2
PPTX
this PowerPoint presentation is all about circles
PPTX
Arcs and angles of circles
PPTX
Presentation on the topic of mathematics - Circle
PPTX
Circle Presentation on a topic in mathematics.pptx
PDF
Grade 9 (Alternate) Mathematics III - Learning Modules for EASE Program of DepEd
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Simulation Learning in Health Sciences and Human Service programs at Camosun ...
PPTX
How to perform product search based on a custom field from the Website Shop p...
PDF
"Perfection of a Kind": A New Critical Reading of W.H. Auden’s Epitaph on a T...
PDF
A Study of W. H. Auden’s September 1, 1939
PDF
BP801T BIOSTATISITCS AND RESEARCH METHODOLOGY (Theory) Unit 2 Part 1
PDF
Holm Community Heritage at St Nicholas Kirk - 2025 AGM Minutes (30.04.2025)
PPTX
How to Set Recurring Tasks in Odoo Projects
PPTX
WEEK 2 (2).pptx TLE COOKERY 10 QUARTER 4
PPTX
A Memory of Two Mondays by Arthur Miller
PDF
Intellectual Property Rights I Types (IPR)
PPTX
Drug acting on ANS.pptx (Drug acts on Sympathetic and parasympathetic NS)
PPTX
13 February 2026 - Bullying in education prevalence, impact and responses acr...
PPTX
Renal Physiology- Functional anatomy of Kidney.pptx
PPTX
Renal Physiology- Juxtaglomerular Apparatus.pptx
PPTX
Overview of How to set priority in Odoo 19 Todo
PDF
PHARMACOLOGY 1 ( BP 404 T) Unit 1 (Cology 1)
PDF
3-ACES-Hyderabad-Vs-Municipal-Corporation-Hyderabad-on-2-Sep-1994.pdf
PDF
Four Stars Of Destiny By General Manoj Mukund Naravane
PPTX
Plant fibres used as surgical dressings & Sutures – Surgical Catgut and Ligat...
PDF
Family and Marriage __ Sociology __ Jhasketan Kuanar __ NURSING VIBE ONLY .pdf
Mathematics CHORDS, ARCS AND ANGLES.pptx 1. 2. CIRCLE
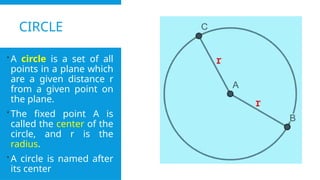
A circle is a set of all
points in a plane which
are a given distance r
from a given point on
the plane.
The fixed point A is
called the center of the
circle, and r is the
radius.
A circle is named after
its center
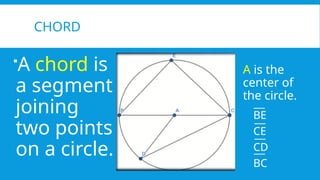
3. CHORD
A chord is
a segment
joining
two points
on a circle.
A is the
center of
the circle.
BE
CE
CD
BC
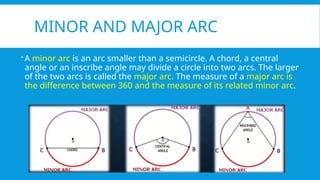
4. MINOR AND MAJOR ARC
A minor arc is an arc smaller than a semicircle. A chord, a central
angle or an inscribe angle may divide a circle into two arcs. The larger
of the two arcs is called the major arc. The measure of a major arc is
the difference between 360 and the measure of its related minor arc.
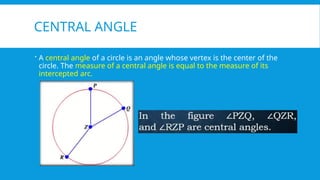
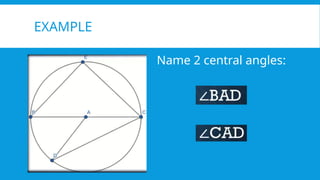
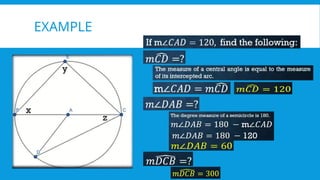
5. 6. CENTRAL ANGLE
A central angle of a circle is an angle whose vertex is the center of the
circle. The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of its
intercepted arc.
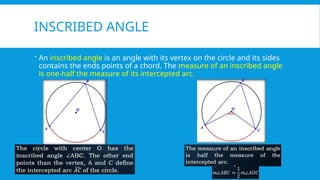
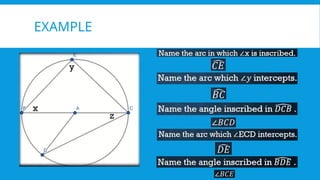
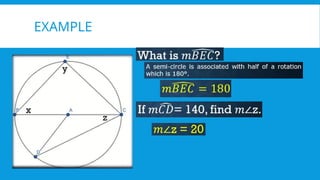
7. 8. INSCRIBED ANGLE
An inscribed angle is an angle with its vertex on the circle and its sides
contains the ends points of a chord. The measure of an inscribed angle
is one-half the measure of its intercepted arc.
9. 10. 11.