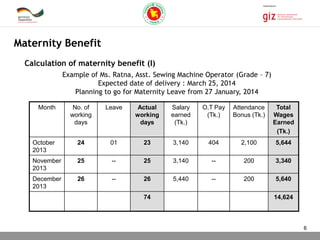
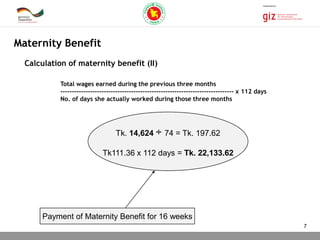
The document outlines the regulations surrounding maternity benefits for women employed in establishments, including a prohibition on working for eight weeks post-delivery and eligibility criteria for receiving maternity benefits. It details the procedures for notifying employers, calculation methods for determining benefit amounts, and the responsibilities of female workers to ensure compliance. Failure to provide maternity benefits can lead to significant financial and health repercussions for workers, as well as legal violations for employers.