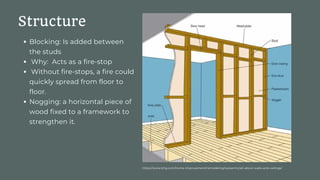
The document discusses stud walls, which are framed walls constructed from vertical wooden or steel studs. It describes the basic components of a stud wall including vertical studs, top and bottom plates, and blocking. Stud walls are used to divide interior spaces, provide insulation and soundproofing, and allow for interior finishes to be applied. The document outlines the materials, typical dimensions, and step-by-step construction process for installing stud walls. It also discusses detailing considerations and the use of double layered drywall for additional sound insulation and impact resistance.