- The document proposes an improved spreadsheet-based mashup tool that allows for distributed spreadsheet composition and always-on functionality to automatically update spreadsheets even when components are offline.
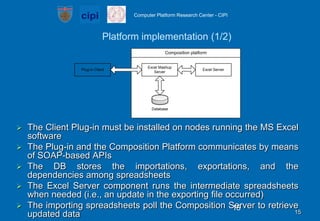
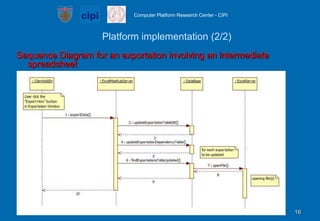
- It describes a platform architecture with a centralized server that manages user accounts and synchronizes data across spreadsheets, and a client plugin that allows importing/exporting data.
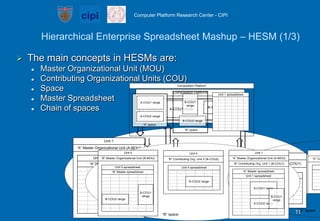
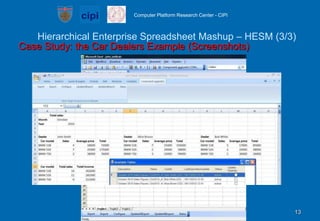
- A case study illustrates how the tool can model the hierarchical structure of a car dealers enterprise where spreadsheets at different organizational levels are composed together.