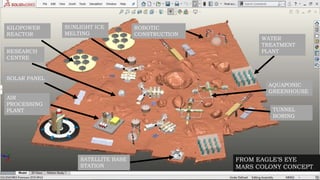
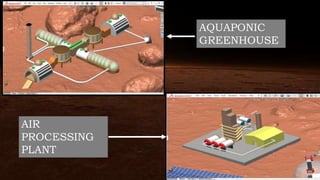
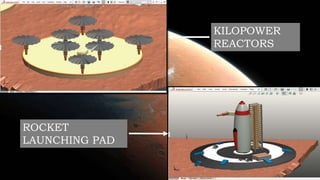
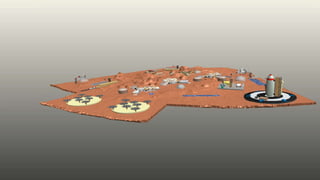
The document compares the climatological and atmospheric characteristics of Mars and Earth, highlighting Mars's thin, carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere and extreme temperatures. It discusses various technologies for establishing a Mars colony, including kilopower reactors for energy, MOXIE for oxygen production, and systems for water treatment and air processing. Additionally, it mentions the importance of communication infrastructure and research facilities for studying Mars and advancing in-situ resource utilization.