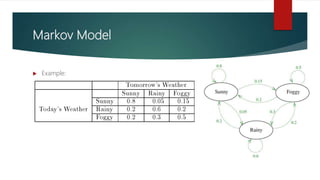
This document provides an introduction to Markov models and hidden Markov models. It explains that Markov models make the assumption that the probability of future states depends only on the present state, not on the sequence of events that preceded it. This allows weather prediction to be modeled based on the probability of today's weather given only yesterday's weather. Hidden Markov models add the complexity that the true states are hidden and can only be inferred from observable events, like whether an umbrella was carried based on the actual sunny, rainy, or foggy weather. The document gives examples of calculating state probabilities using these types of models.