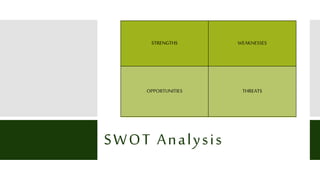
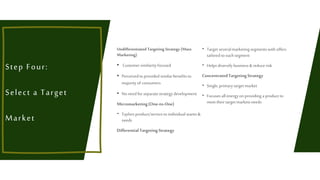
This document outlines the five steps of an STP (segmentation, targeting, positioning) analysis process used by companies to identify their ideal customer base. The five steps are: 1) establish marketing strategy objectives, 2) use segmentation methods to divide the market into subgroups, 3) evaluate segment attractiveness, 4) select a target market, and 5) develop a positioning strategy to communicate the product's value proposition to the target market. The goal is to help companies focus on customers and position offerings to meet customer needs better than competitors.