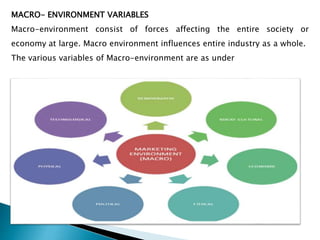
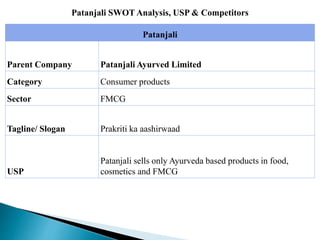
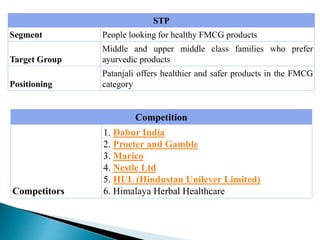
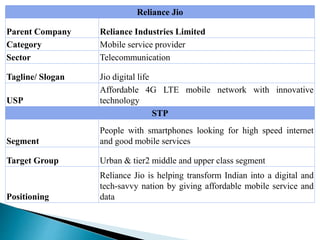
The document discusses the key concepts of marketing including definitions of marketing, the marketing concept, and the evolution of marketing philosophies over time. It provides definitions of marketing from various organizations and experts. It describes the progression from a production concept focused on mass production to a selling concept focused on persuading customers, to today's customer-centric marketing concept focused on satisfying customer needs. The functions, scope, and importance of marketing are also summarized.