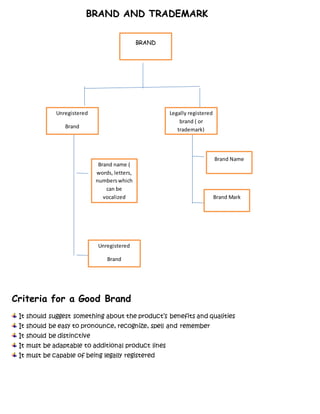
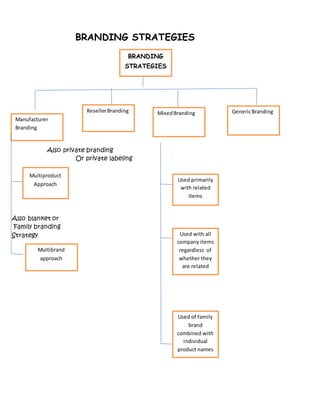
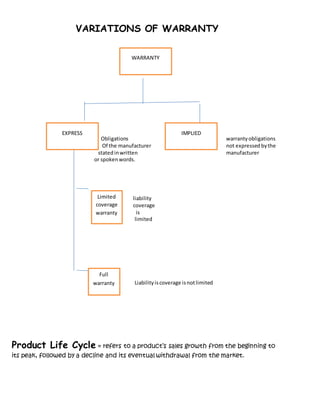
This document discusses various marketing concepts related to products and branding. It defines a product as anything offered for sale to satisfy customer needs. It then outlines the product life cycle and various stages (introduction, growth, maturity, decline). It also discusses branding strategies manufacturers and resellers can use. Branding identifies and differentiates a seller's goods/services, and branding criteria include being pronounceable, distinctive, and legally registrable. Packaging and labeling are also summarized in terms of their purposes and types.