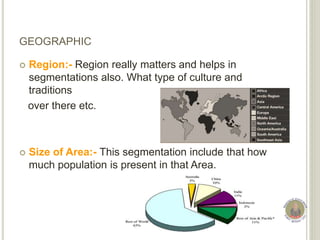
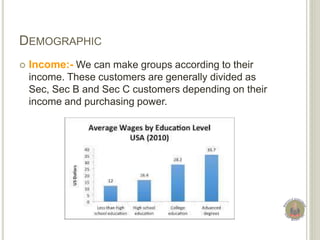
Market segmentation involves dividing a market into homogeneous groups based on criteria like geography, demographics, psychographics, and behavior. It allows organizations to target desirable customer segments. Key criteria for segmentation include segments being measurable, accessible, large enough for profit potential, and stable over time. Common bases for consumer segmentation are geographic variables like region and climate, demographic factors like age, gender, and income, psychographic attributes like lifestyle and interests, and behavioral patterns like purchase occasions and loyalty. Effective segmentation allows customized marketing strategies for each group.