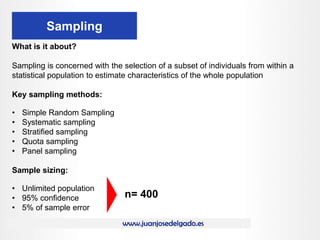
The document provides a comprehensive overview of market research, detailing its functions, methods, and tools. It describes techniques such as focus groups, surveys, and observational methods, along with their benefits, and outlines the steps involved in the marketing research process from defining the problem to making decisions based on findings. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of proper sampling, data collection, and analysis to derive actionable insights.