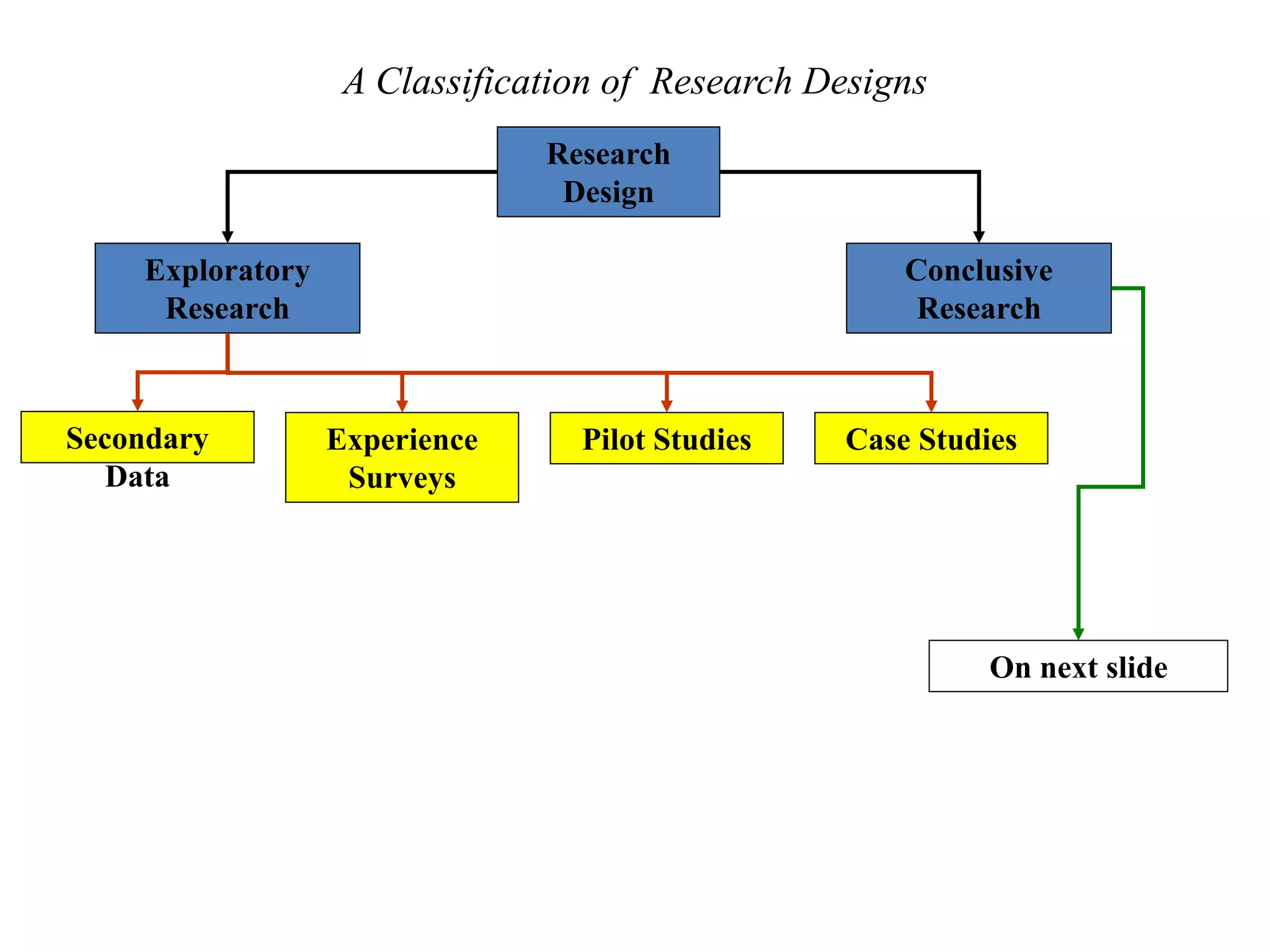
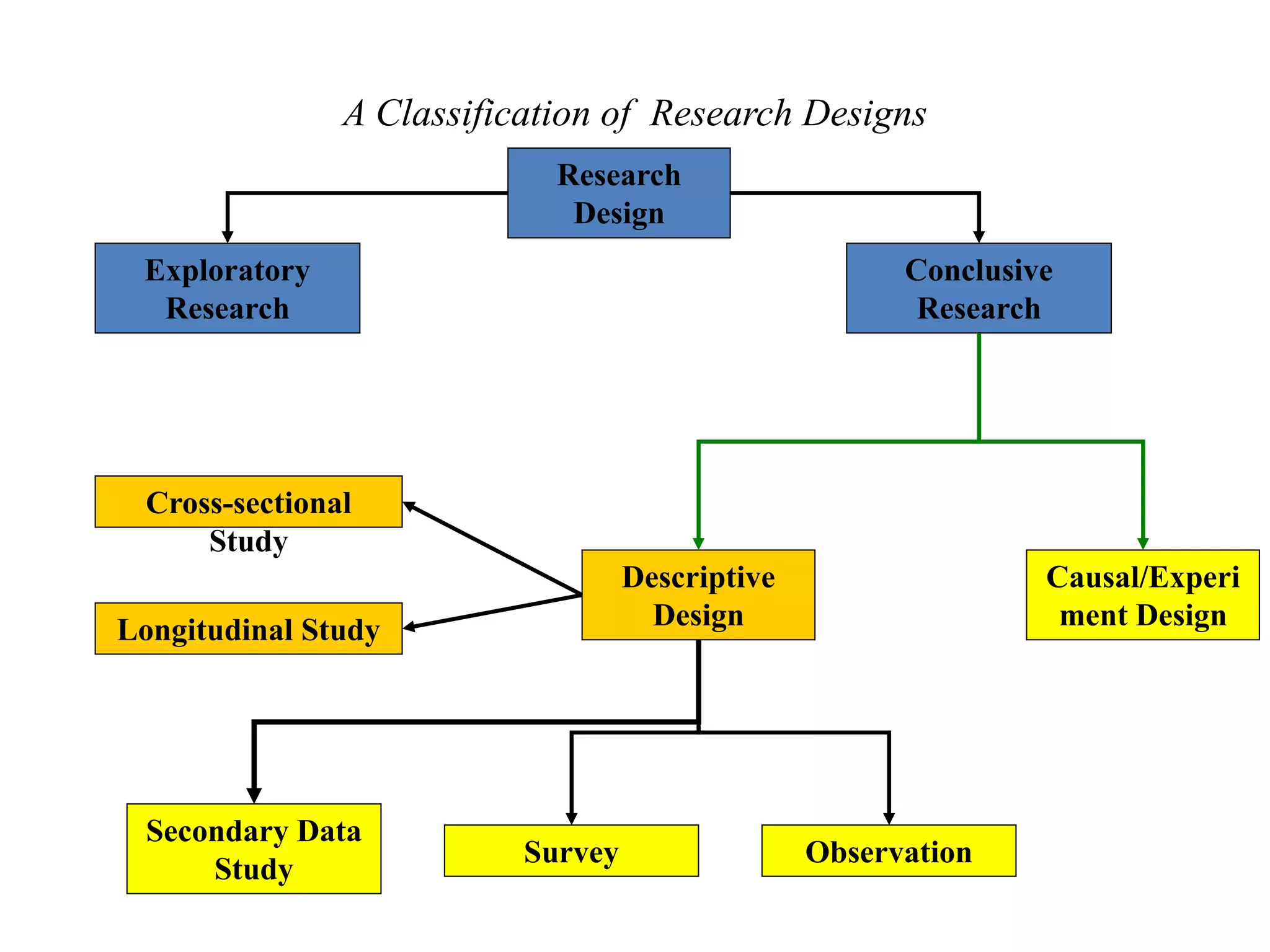
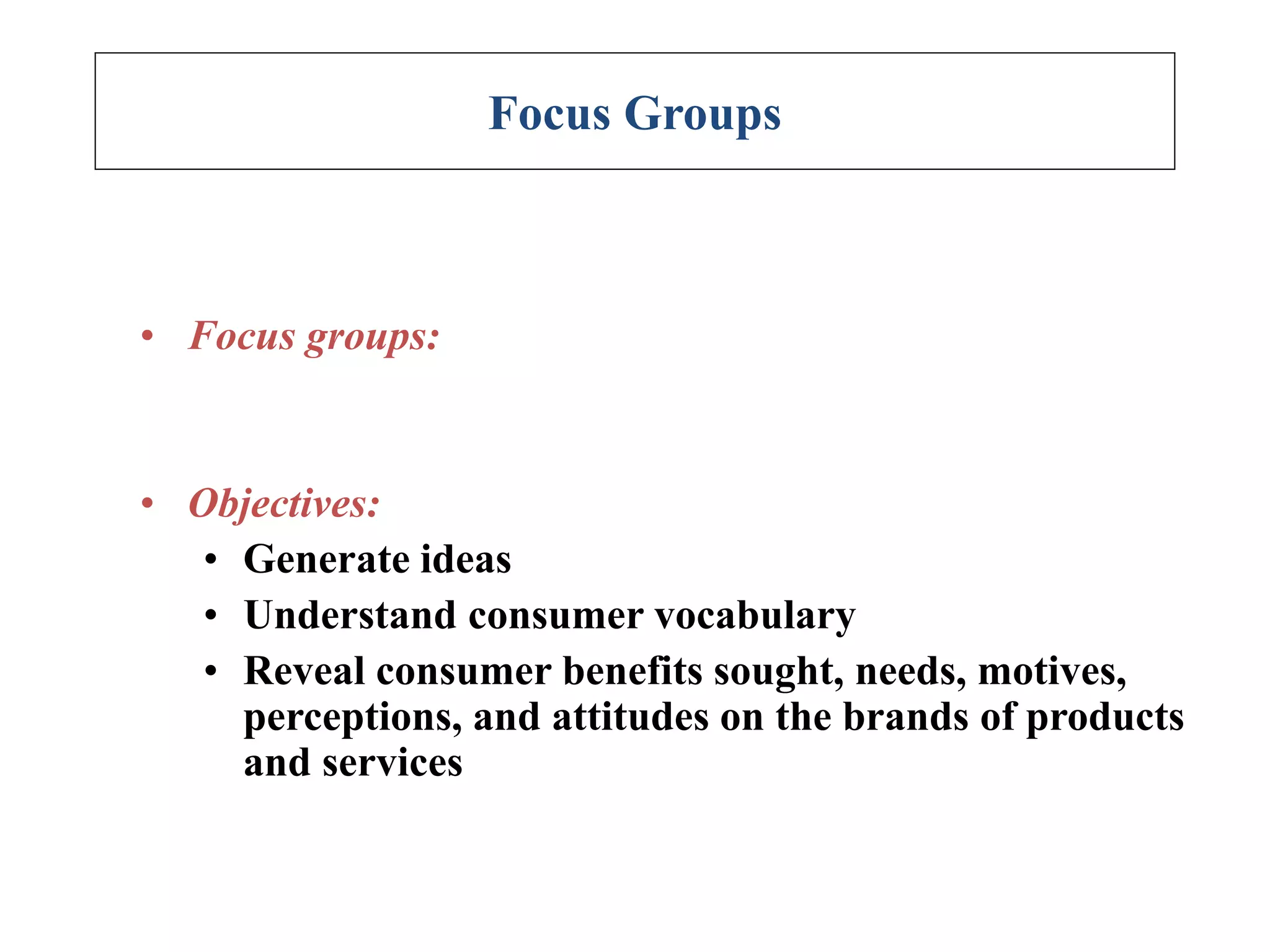
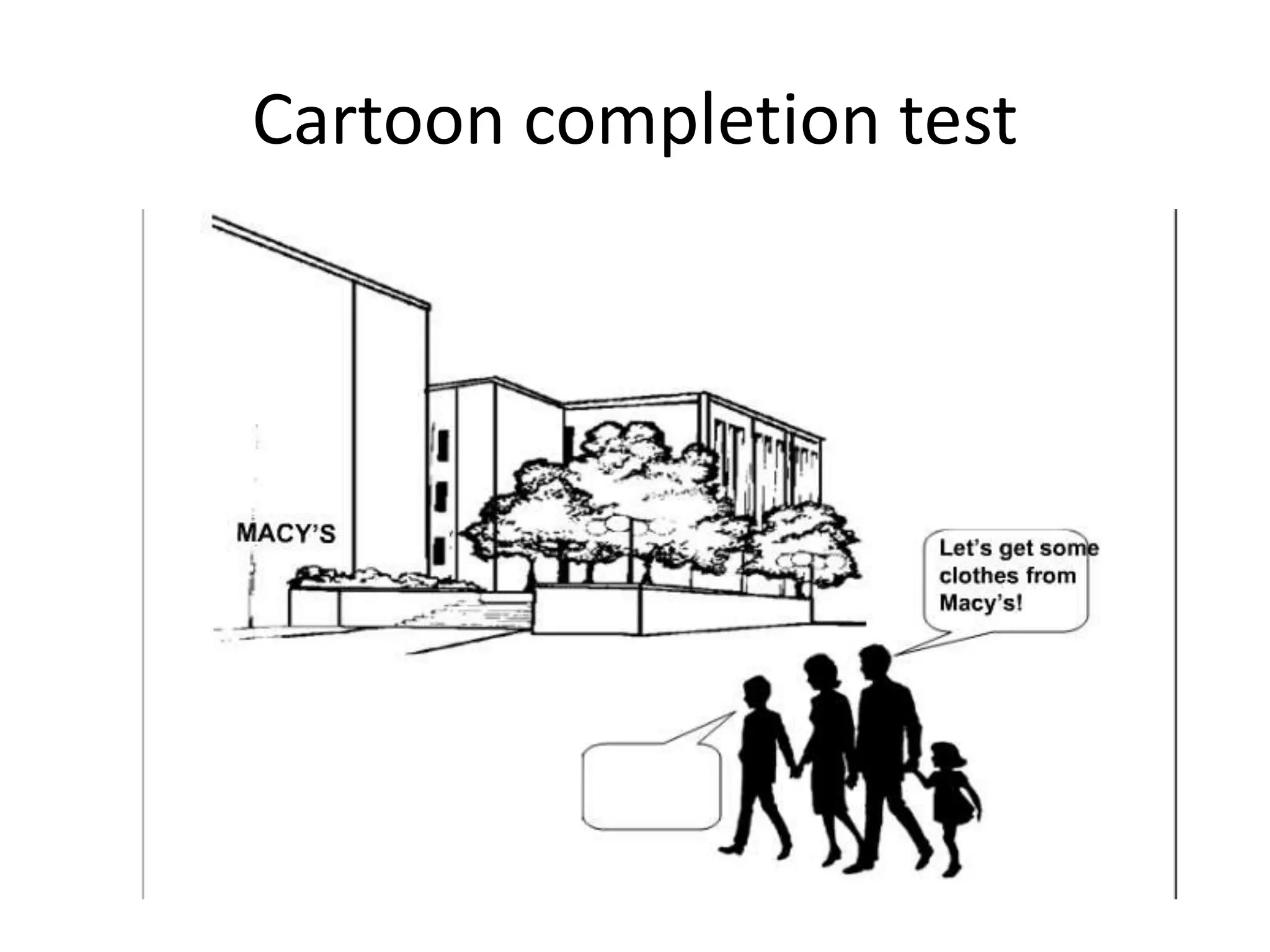
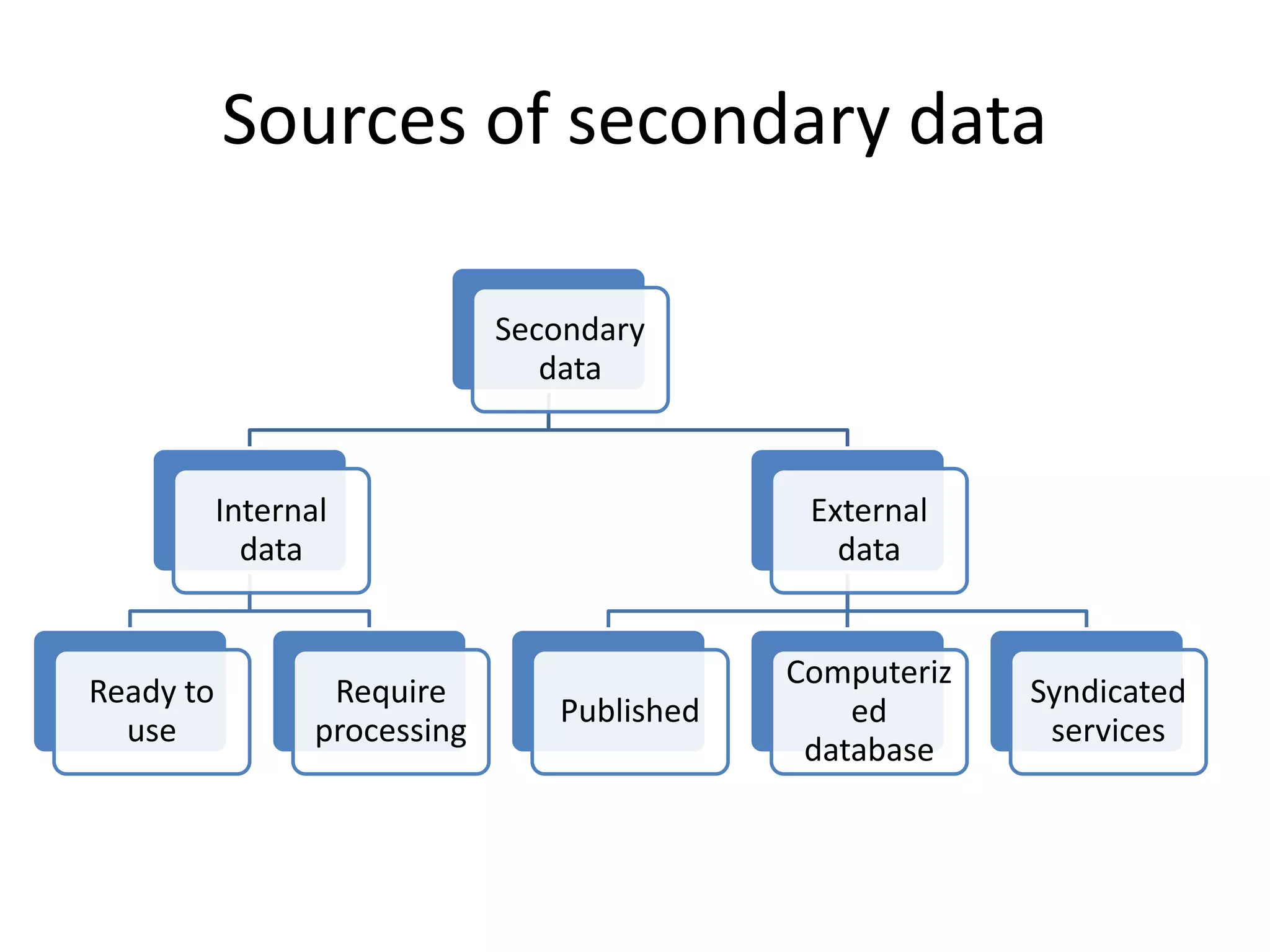
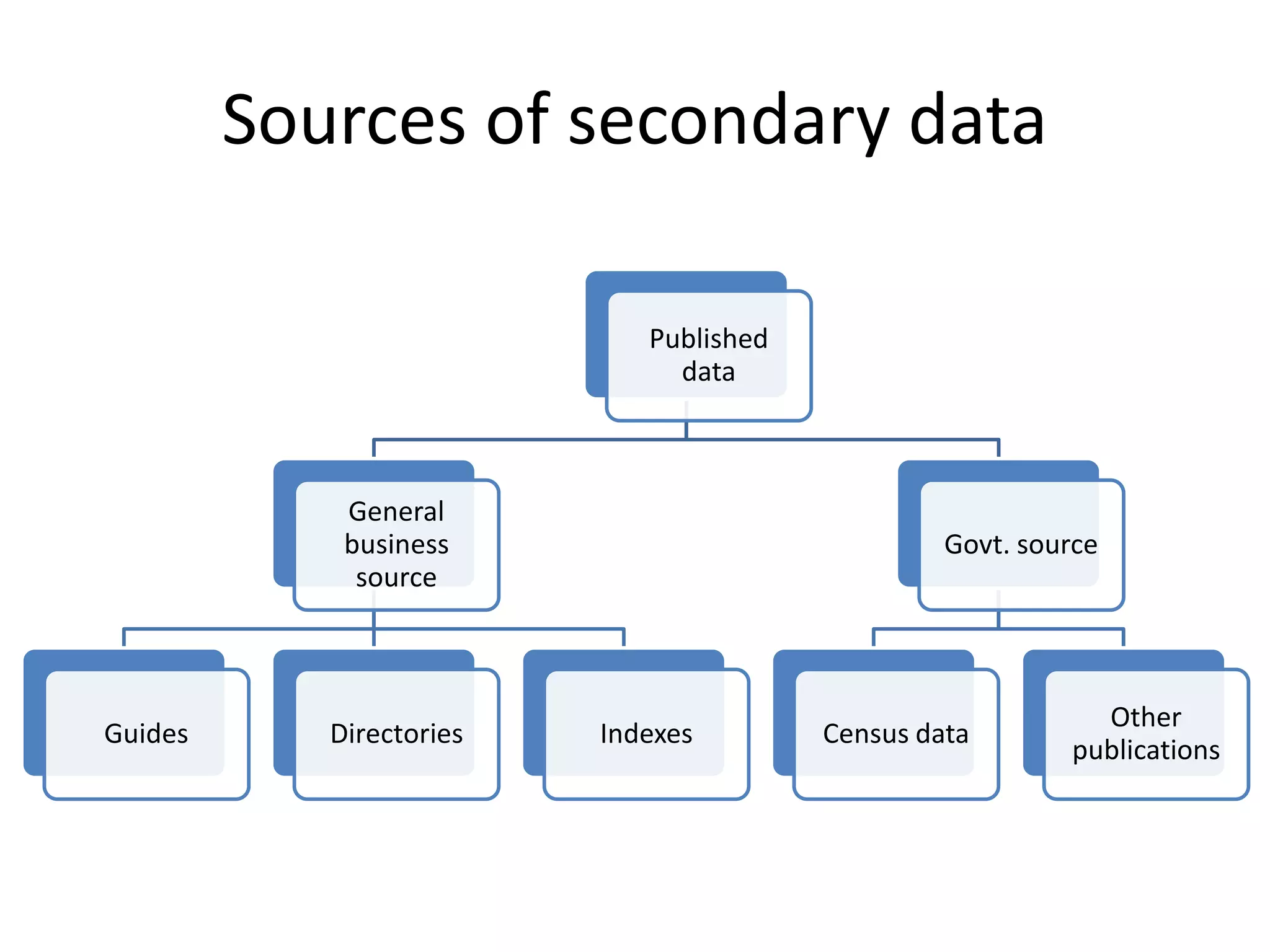
The document discusses different types of research designs used in research projects. It describes exploratory research, descriptive research, and causal/experimental research. Exploratory research is conducted to gain insights and ideas when the problem is not clearly defined. Descriptive research aims to obtain summary measures to address clearly defined research objectives. Causal/experimental research examines cause-and-effect relationships between decisions and outcomes. The choice of research design depends on the objectives and what is known about the problem. Common exploratory techniques include surveys, focus groups, in-depth interviews, case studies, and secondary data analysis.