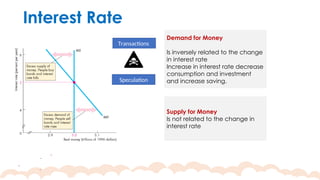
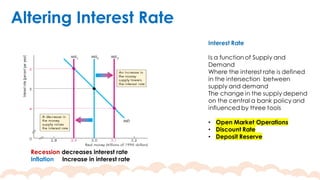
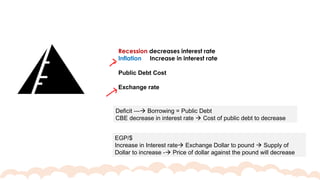
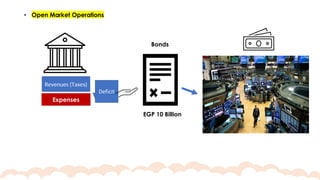
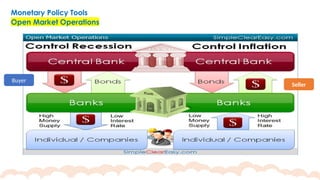
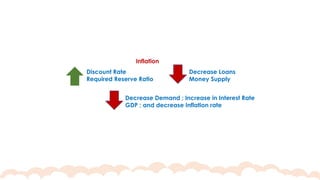
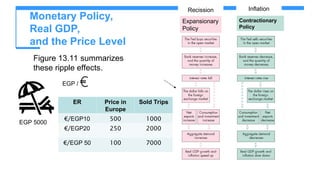
This chapter covers the objectives and tools of monetary policy, explaining the mechanisms of open market operations, the demand for money, and the role of central banks in controlling interest rates. It discusses the relationship between interest rates, spending, GDP, inflation, and public debt. The chapter highlights the impact of monetary policy on the economy, including how changes in rates influence consumption, investment, and overall economic growth.