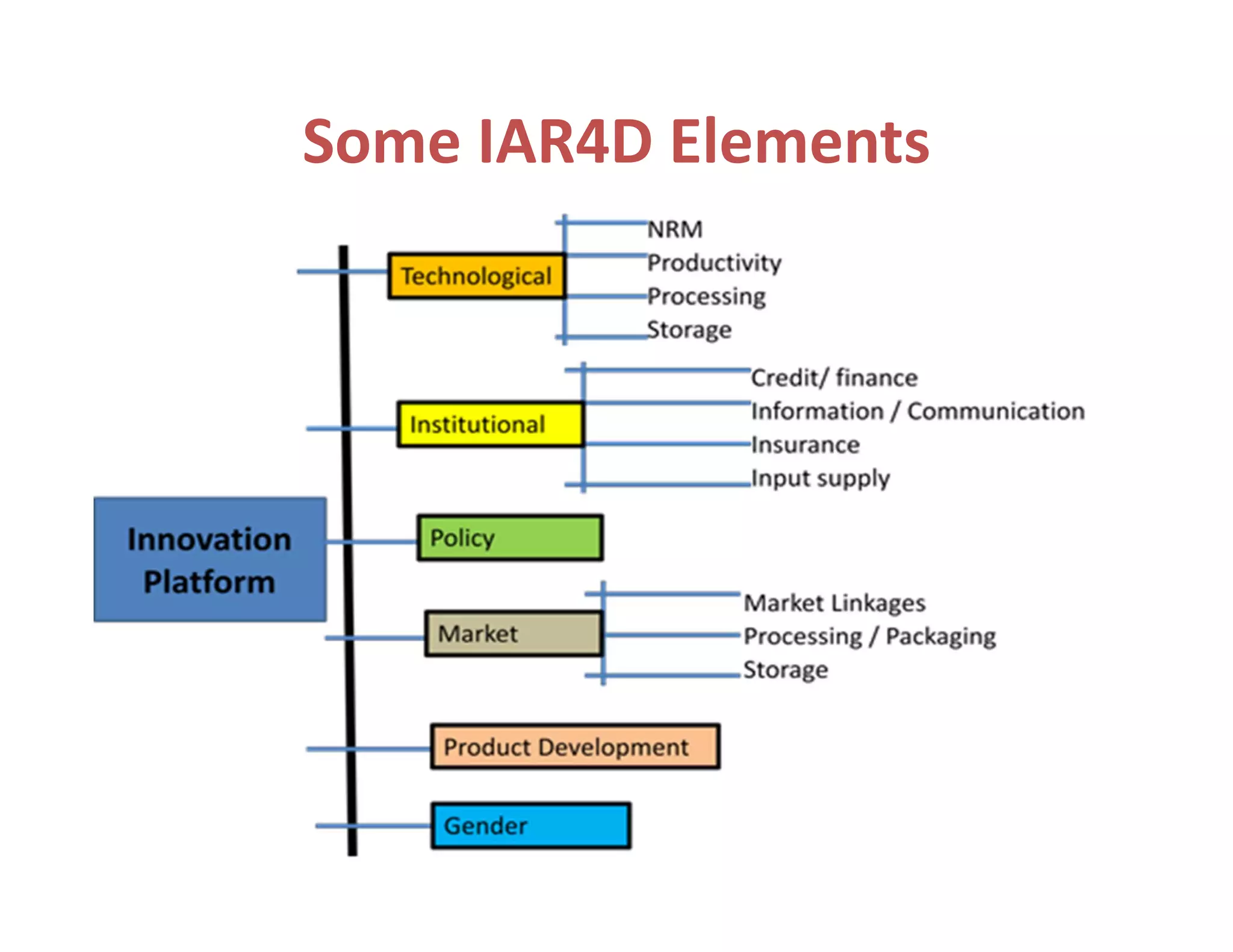
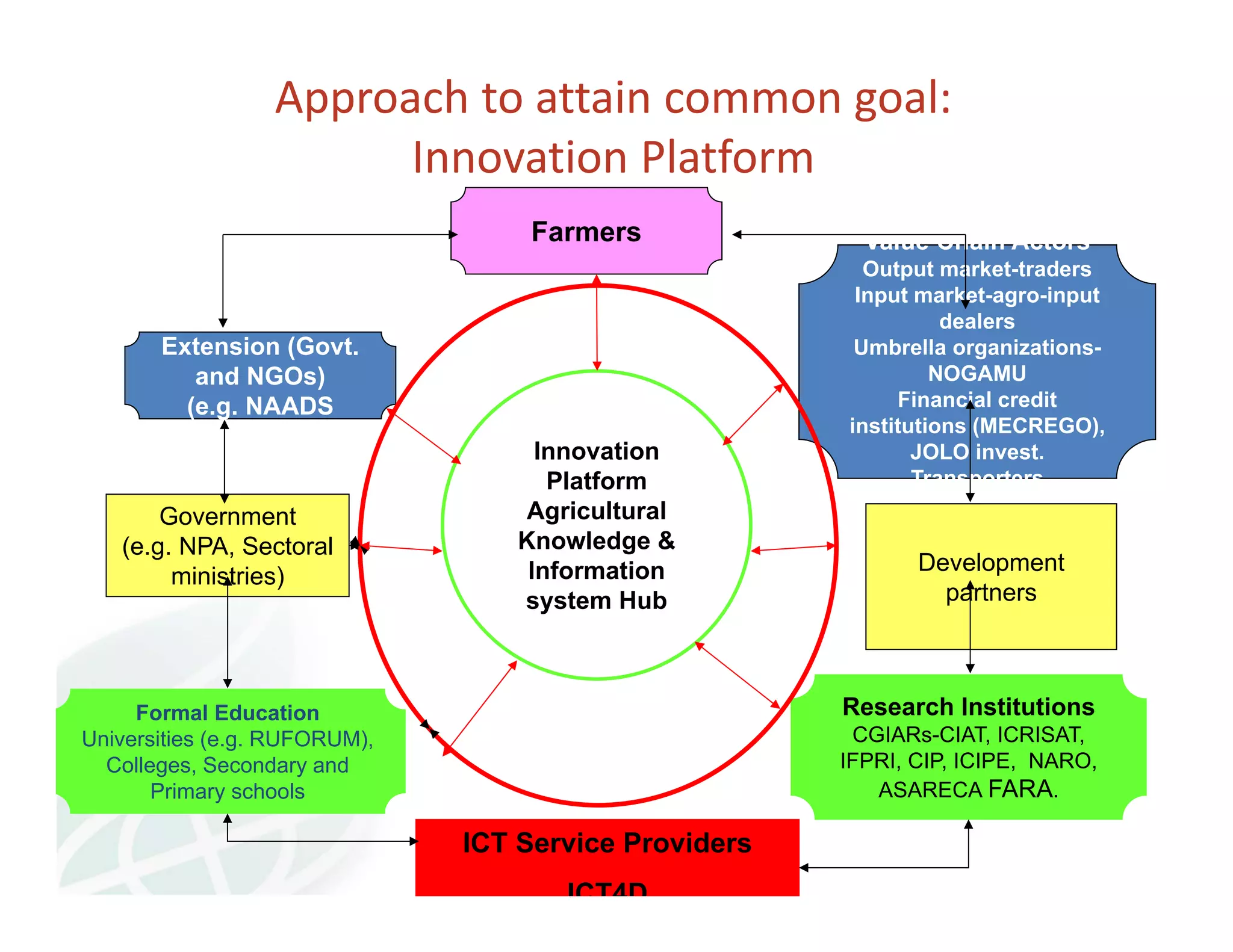
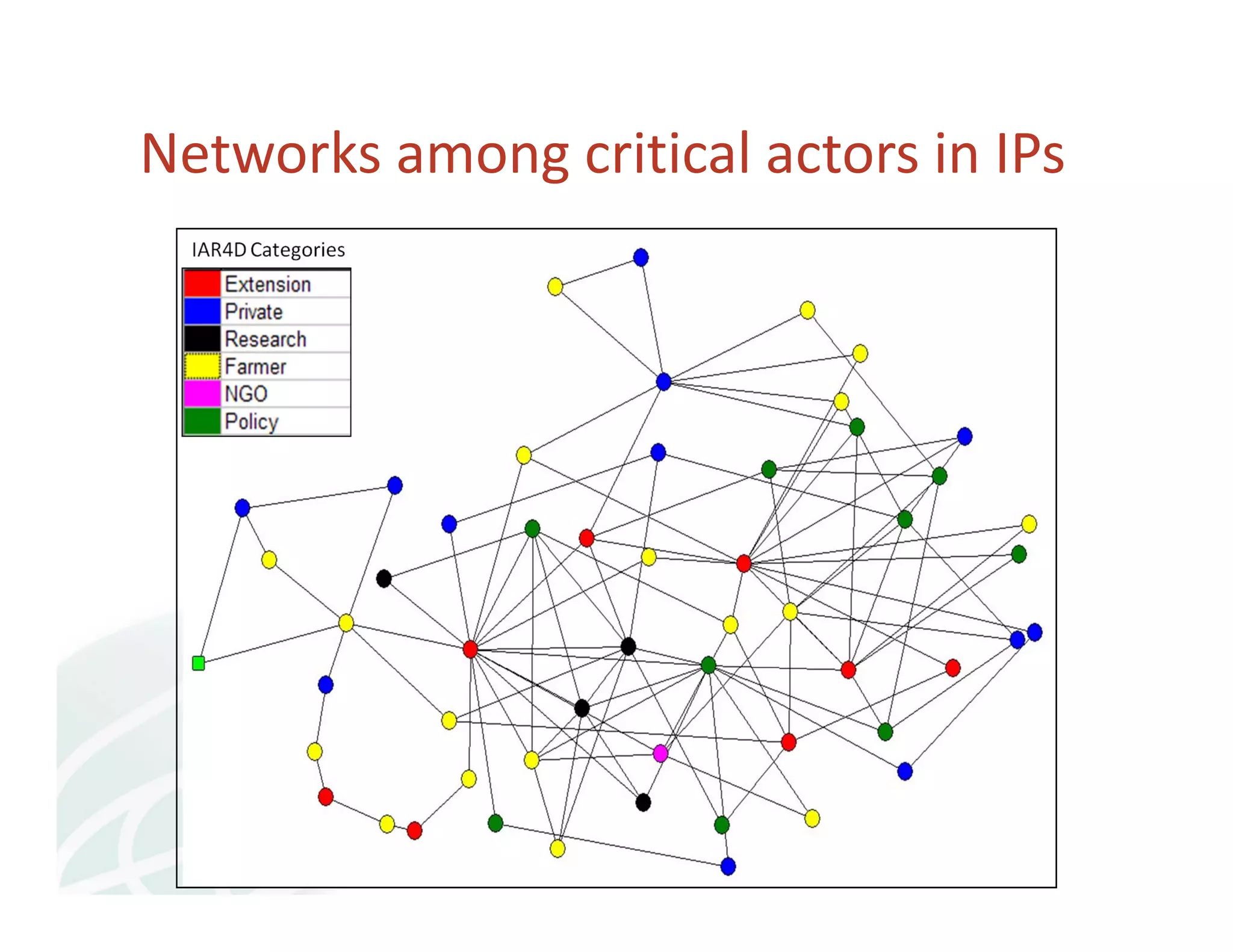
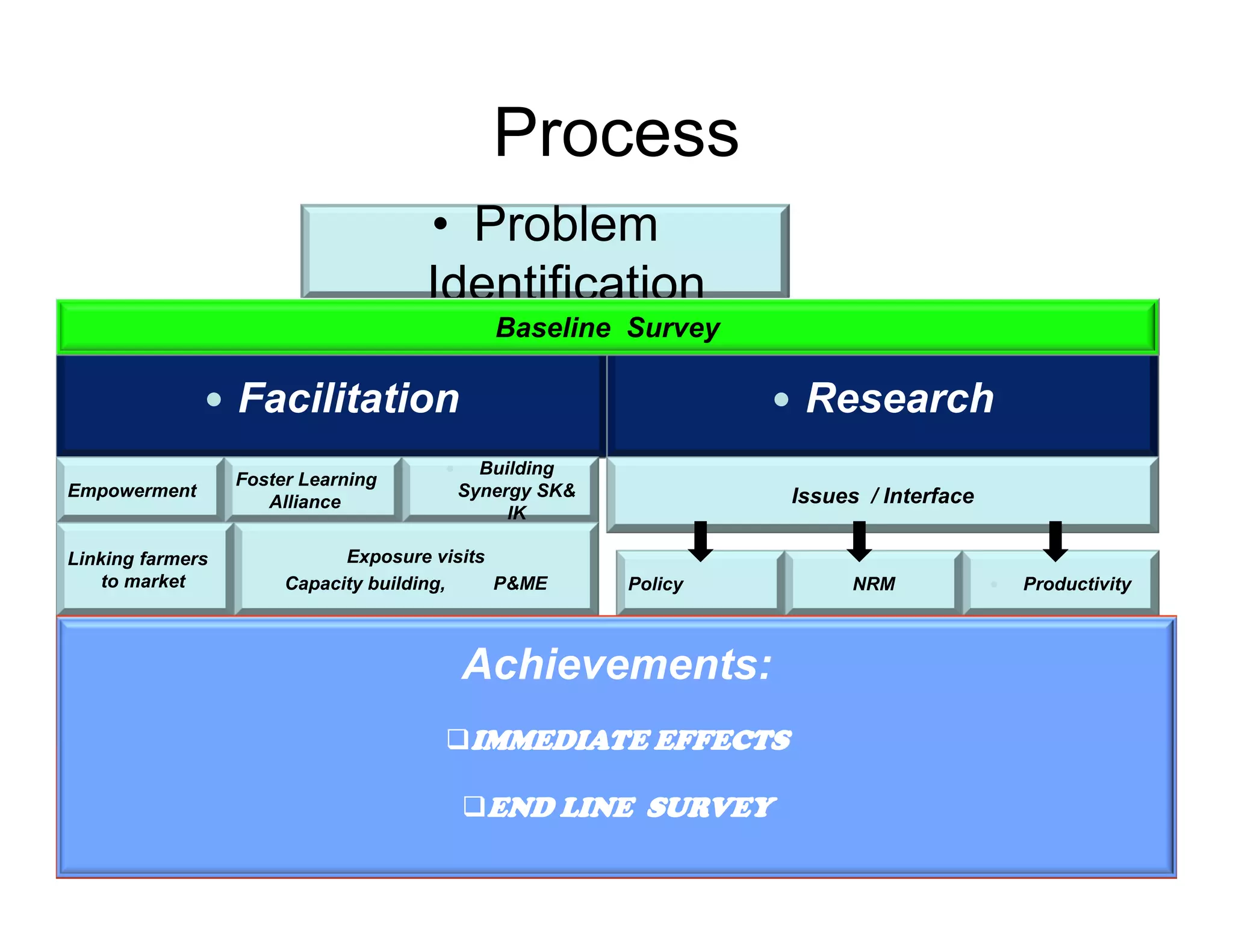
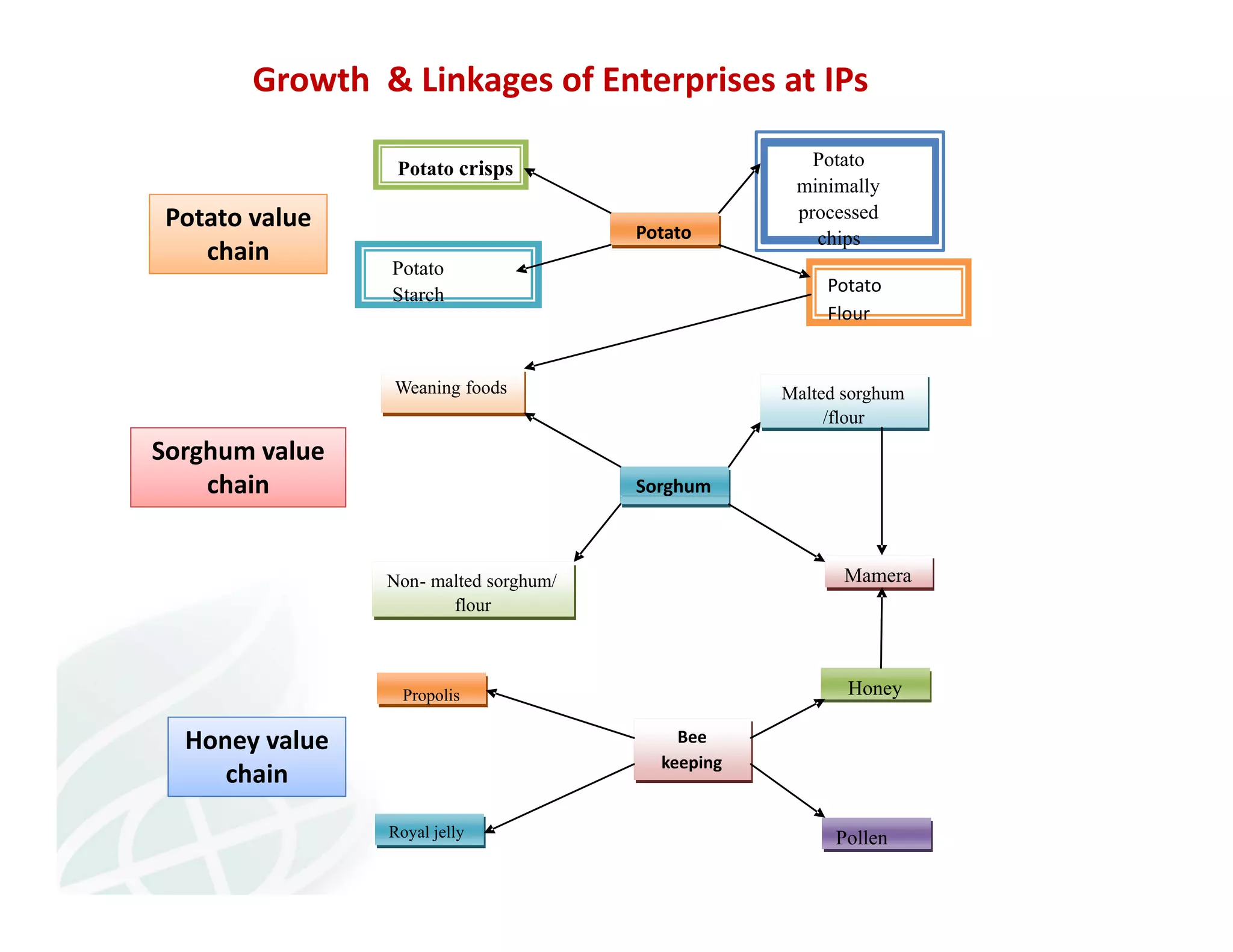
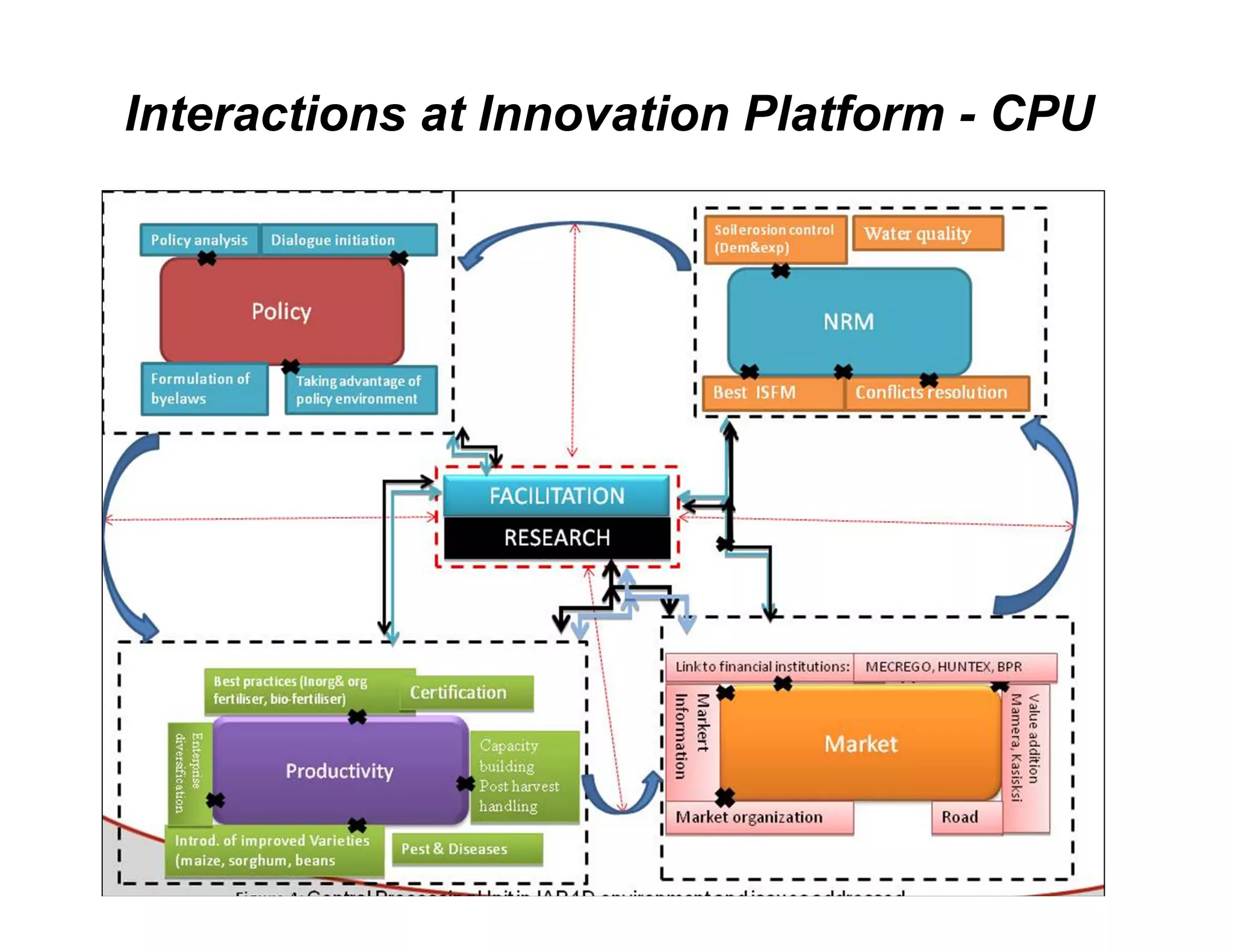
The document discusses innovation platforms (IPs) that bring together different stakeholders along agricultural value chains to jointly solve problems. It provides an overview of the implementation of the Integrated Agricultural Research for Development (IAR4D) concept through the Sasakawa Africa Fund-supported project in three phases since 2004. The project used IPs as operational instruments to foster interactions between actors like farmers, traders, researchers and policymakers to increase innovation and promote scaling up of solutions. Some lessons learned include that market-led processes catalyzed innovations, quality facilitation influenced innovation, and policy support was useful for involvement.