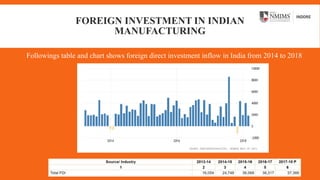
The document discusses the Make in India initiative launched in 2014 with the goal of making India a global manufacturing hub. It aimed to increase manufacturing's GDP contribution to 25% and create 100 million jobs. While foreign investment and several sectors saw growth, the program has faced challenges in fully delivering due to issues like low productivity, skills shortages, regulations, and infrastructure problems. Suggestions to improve it include reducing taxes, enhancing ease of doing business, and creating a more innovation-friendly environment. In conclusion, Make in India could still achieve its vision but requires coordinated government support through policy reforms.