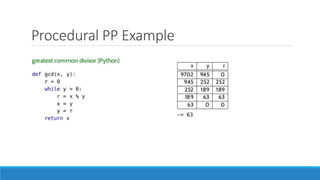
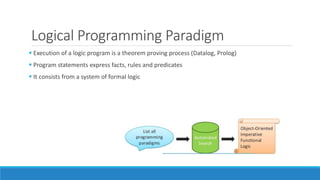
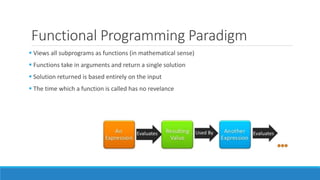
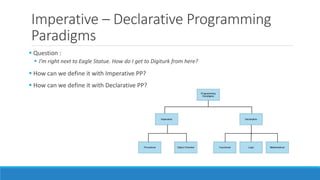
The document discusses major programming paradigms, focusing on imperative and declarative types, and outlines four key paradigms: procedural, object-oriented, logical, and functional programming. It emphasizes the differences between imperative (how to do something) and declarative (what to do) programming through various examples. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each paradigm, providing insights into their applications and efficiency.










![Examples of PP with
Programming Languages
Javascript (write a function called double which takes an array, and return a new array where
the values doubled) :
function double (arr) {
let results = []
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
results.push(arr[i] * 2)
}
return results
}
function double (arr) {
return arr.map((item) => item * 2)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/majorprogrammingparadigms12022020-211013210721/85/Major-Programming-Paradigms-12-320.jpg)