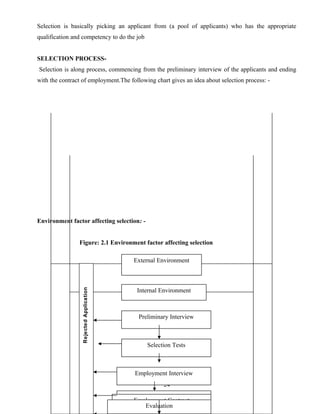
This document discusses the recruitment and selection process at MotilalOswal in Hyderabad, India. It begins with an introduction to human resource management and recruitment. The recruitment process involves identifying vacancies, defining job requirements, advertising positions, managing responses, shortlisting candidates, conducting interviews, making hiring decisions, and onboarding new employees. The objectives of the study are to evaluate MotilalOswal's recruitment and selection process, understand employees' attitudes, and make suggestions for improvement. The review of literature provides background on recruitment, the importance of an effective process, and the typical stages involved, from planning to evaluation.




































![and corporate clients. We are headquartered in Mumbai and as of March 31st, 2012,
had a network spread over 612 cities and towns comprising 1,644 Business Locations
operated by our Business Partners and us. As at March 31st, 2012, we had 709,041
registered customers.
MotilalOswal Financial Services Ltd., is a non-banking financial company [NBFC]
register under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The company’s stand alone
operations are
i. Build on a financing infrastructure that can best customize risk adjusted products.
ii. Have simple and compliant documentation and prompt loan approval procedures.
iii. A strong structure in place that can most efficiently source funds and manage
resources.
MILESTONES:
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maindacument-140804094529-phpapp02/85/Main-dacument-41-320.jpg)
































![APPENDIX
QUESTIONNAIRE
Dear Employee,
I am N.HAMSALEKHA pursuing MBA (IV SEM) from PRINCETON PG COLLEGE
OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY. As part of the curriculum, I have taken up HR
project work “Recruiting Process” at hero motors .HYDERABAD I request you to
support by taking some time off your busy schedule and filling up this questionnaire.
1. Are you aware of the objectives of the organization? [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) No [ ] c) No idea [ ]
2. Are you aware of recruitment process of the organization? [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) No [ ] c) No idea [ ]
3. Training and development programs acts as the best tool to reach the standard
level of performance. [ ]
a) Agreed [ ] b) disagree [ ] c)No idea [ ]
4. Policies and practices adopted by the HR department are good. [ ]
a) Agreed [ ] b) disagree [ ] c) No idea [ ]
5. Communication system in the organization is effective [ ]
a) Agreed [ ] b) disagree [ ] c) No idea [ ]
77](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maindacument-140804094529-phpapp02/85/Main-dacument-77-320.jpg)
![6. My department has effective procedures to guide my day-to-day work. [ ]
a) Agreed [ ] b) disagree [ ]c) No idea [ ]
7. I am satisfied by the recruitment process carried out by the organization [ ]
a) Agreed [ ] b) disagree [ ] c) No idea [ ]
8. I reach the monthly target closers of the organization [ ]
a) Agreed [ ] b) disagree [ ] c) No idea [ ]
9 How many profiles do you shortlist per a day [ ]
a) 0-5 [ ] b) 6-10 [ ] c) more than 10 [ ]
10. Do you like to share the applicant information with the third party vendors [ ]
a) Agreed [ ] b) disagree [ ] c) No idea [ ]
11. Do you have the applicants tracking system in the organization? [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) no [ ] c) No idea [ ]
12. Is it possible to measure the applicant confidence and technical skill level
before short listing? [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) No[ ] c) No opinion [ ]
13. Is it helpful to maintain profiles database. [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) No [ ]c) No opinion [ ]
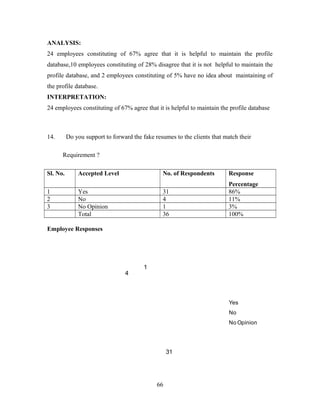
14. Do you support to forward the fake resumes to the clients that match their
78](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maindacument-140804094529-phpapp02/85/Main-dacument-78-320.jpg)
![Requirement [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) No [ ] c) No opinion [ ]
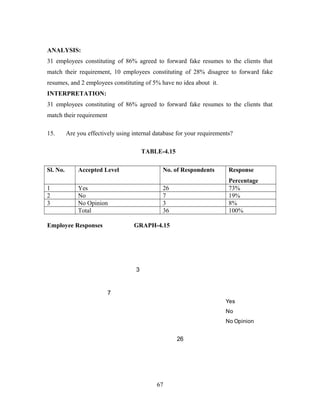
15 Are you effectively using internal database for your requirements. [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) No [ ] c) No opinion [ ]
16. Are you aware of job postings in the portals? [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) No [ ] c) No opinion [ ]
17 From which source you are getting maximum responses [ ]
a) Company database [ ]b) Advertisements[ ] c) Postings in the Job portals[ ]
18. Are you aware of the payments terms? [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) No [ ] c) No opinion [ ]
19. Are you dealing with IT requirements or Non IT Requirements? [ ]
a) IT Requirements [ ] b) Non IT requirements [ ] c) Both [ ]
20. Are you aware of client Information? [ ]
a) Yes [ ] b) No [ ] c) No opinion [ ]
Please give your valuable suggestions/remarks:
79](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maindacument-140804094529-phpapp02/85/Main-dacument-79-320.jpg)
