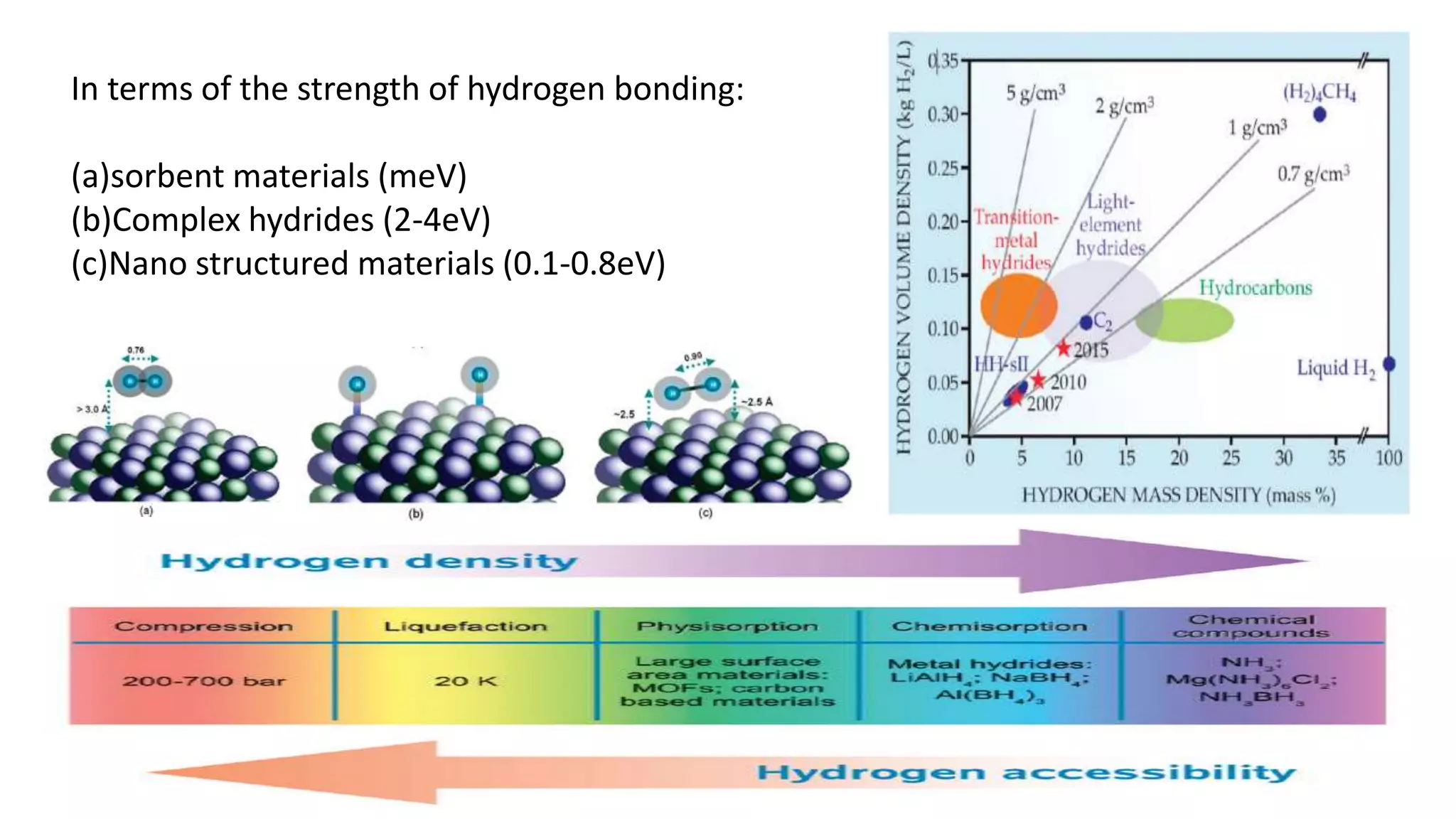
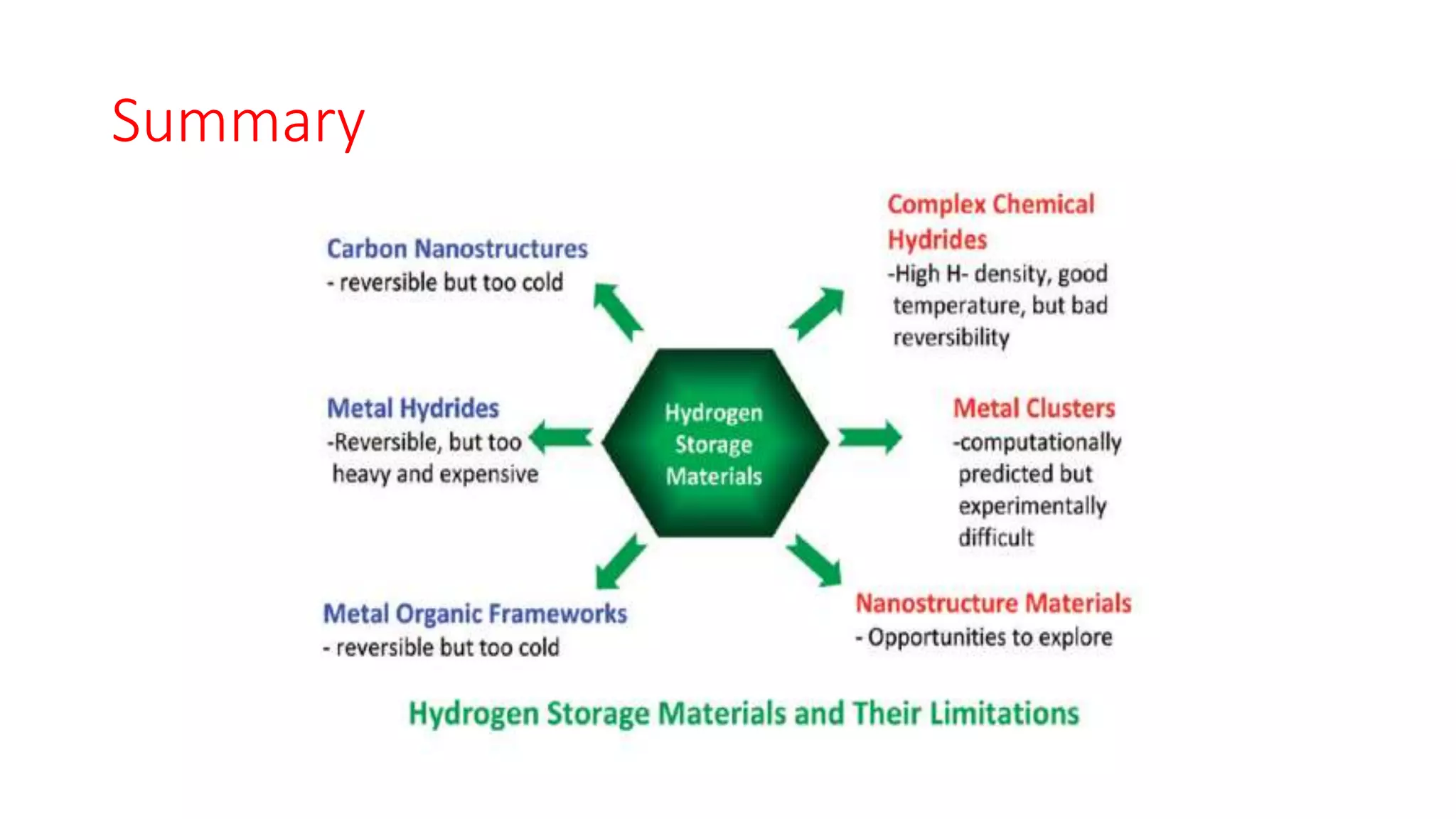
This document discusses materials for hydrogen storage and some of the challenges. It notes that hydrogen is not an energy source itself but an energy carrier, and currently it is stored as either high-pressure gas or cryogenic liquid. Solid materials could provide an alternative storage method. Sorbent materials like carbon nanotubes and metal-organic frameworks can store hydrogen at low temperatures but have low storage capacities at room temperature. Complex hydrides can store more but are heavy, expensive, and only work at high temperatures. Nanostructured materials show potential through properties unlike bulk materials, but have yet to emerge as practical solutions and require more research into catalysts, intermediate phases, and kinetics.