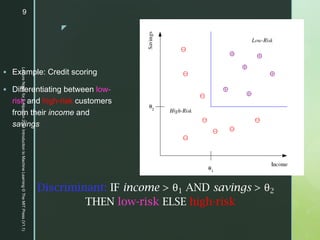
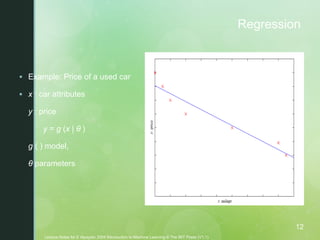
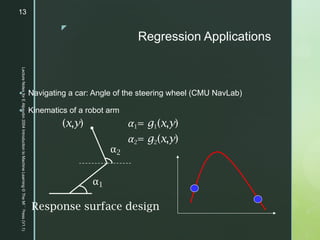
This document provides an introduction to machine learning, including definitions, applications, and resources. It defines machine learning as programming computers to optimize performance using example data or past experience. Applications discussed include classification, regression, association rule learning, clustering, and reinforcement learning. Examples are given for applications in domains like credit scoring, face recognition, medical diagnosis, and game playing. Resources mentioned for machine learning include datasets, journals, and conferences in the field.