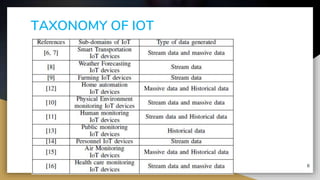
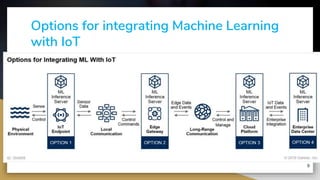
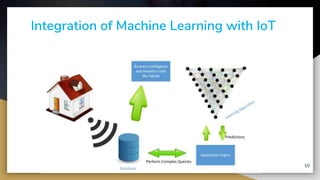
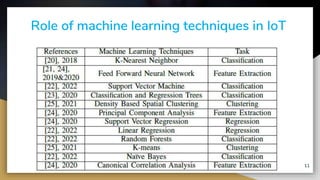
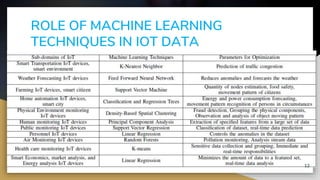
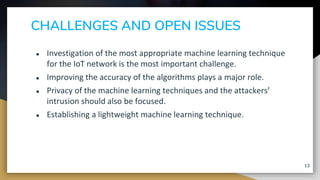
This document provides an overview of machine learning techniques for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It begins with an introduction to the growth of IoT devices and need for analyzing IoT data. It then discusses taxonomy of IoT and machine learning, categorizing supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. The document outlines how machine learning can be integrated with IoT for applications like predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and activity recognition. It also discusses challenges of selecting appropriate machine learning techniques for IoT and improving algorithm accuracy. The conclusion is that machine learning algorithms are well-suited for analyzing and making predictions from smart IoT device data.