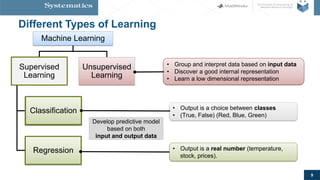
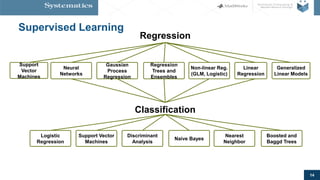
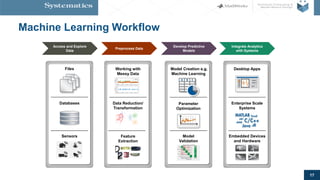
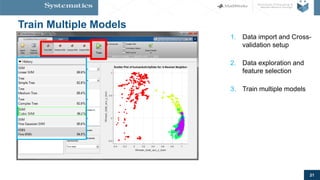
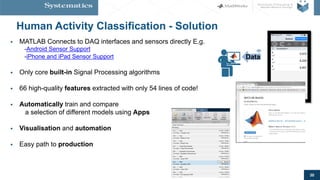
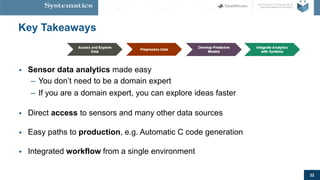
The document provides an overview of machine learning, emphasizing its application in sensor data analytics and human activity classification. It covers different types of machine learning, workflows, challenges, and specific examples that illustrate the importance and versatility of machine learning in various domains. Key takeaways highlight the accessibility of sensor data analytics and the integration of machine learning tools for efficient model development.




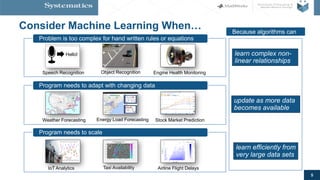
![6
Machine Learning is Everywhere
Stock Prediction
Speech Recognition
Image Recognition
Medical Diagnosis
Data Analytics
Energy
Robotics
and more…
[TBD]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machinelearningforsensordatsanalytics-170724102717/85/Machine-learning-for-sensor-Data-Analytics-6-320.jpg)