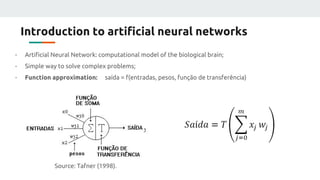
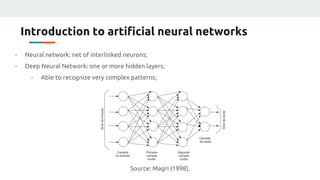
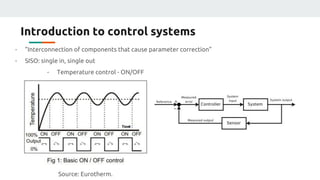
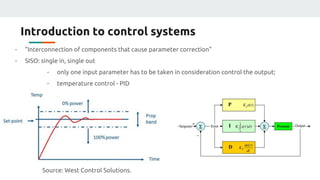
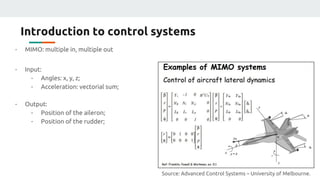
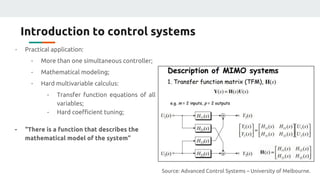
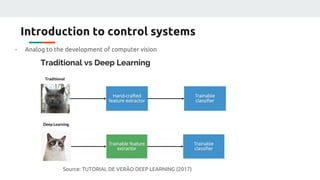
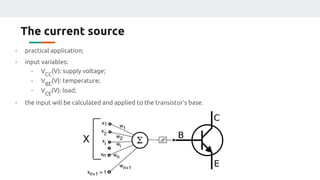
(1) The document discusses applying machine learning and artificial neural networks to control multivariable systems. Specifically, the authors aim to use these techniques to control a current source despite variations in temperature, supply voltage, and load.
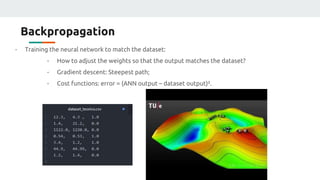
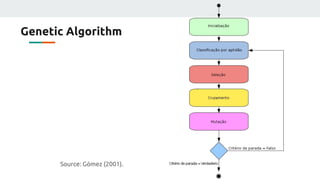
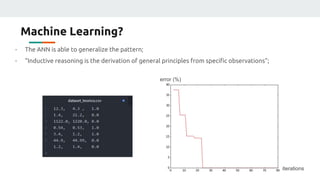
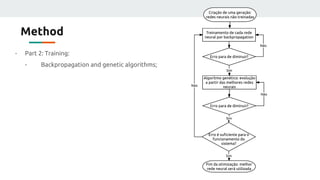
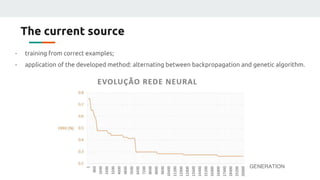
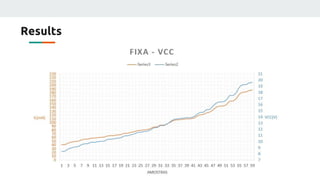
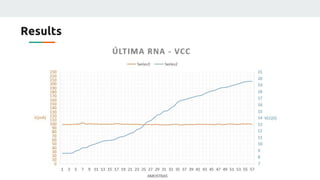
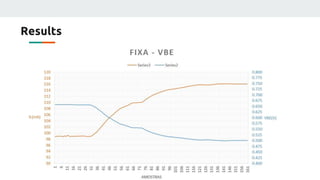
(2) They plan to gather empirical data on the current source's behavior under different conditions and use backpropagation and genetic algorithms to train a neural network to maintain a constant current output.
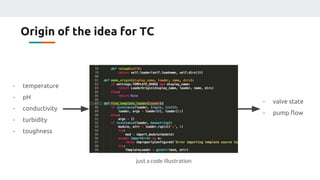
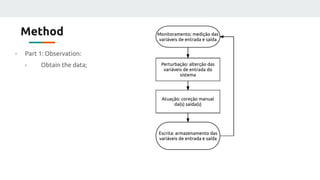
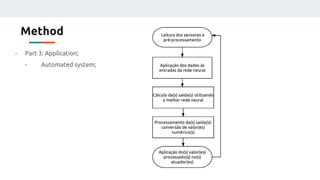
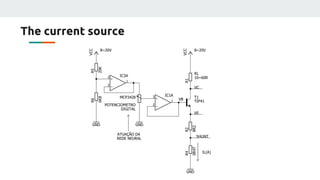
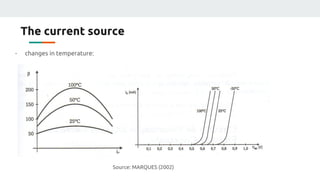
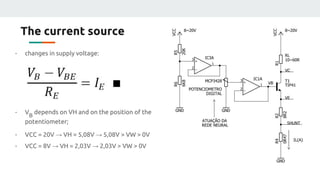
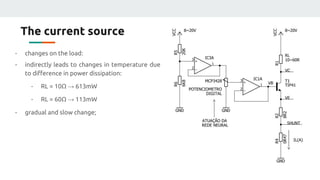
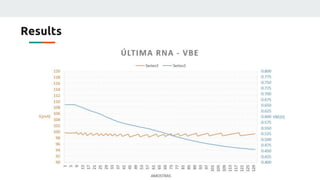
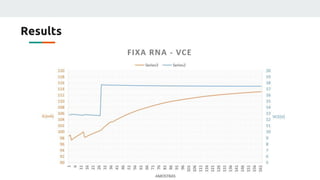
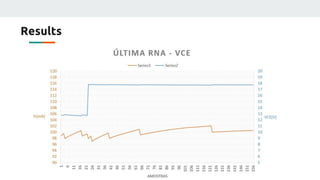
(3) The authors isolated the current source's variables to simplify initial testing - using the neural network to control the potentiometer in response to single variable changes like temperature, voltage, or load. Their goal is for the network to eventually handle variations in all variables simultaneously.