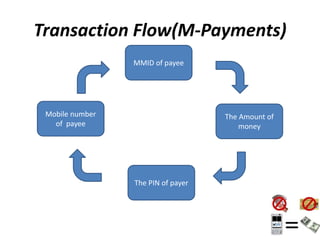
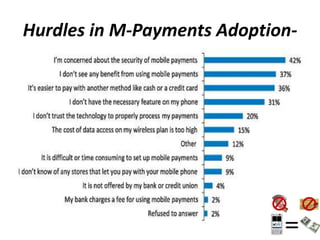
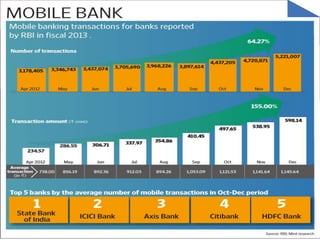
M-Payments allow customers to pay for goods and services using their mobile phones instead of cash, checks, or credit cards. Major banks in India offer M-Payment services that allow customers to send money via SMS, Java applications over GPRS, or WAP. The services use technologies like premium SMS, direct mobile billing, mobile web payments, and NFC. Regulations in India require that only banks licensed and physically present in India can offer these services, which must be in Indian rupees and follow KYC and AML guidelines. Customers must register with their bank before using M-Payment services.