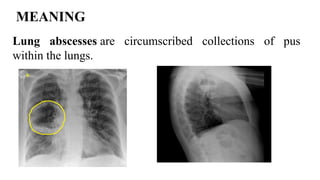
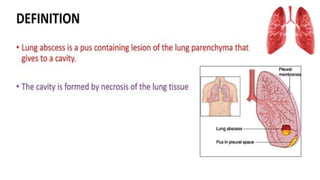
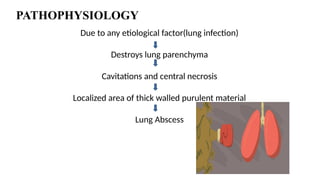
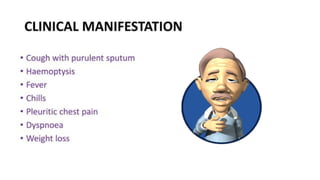
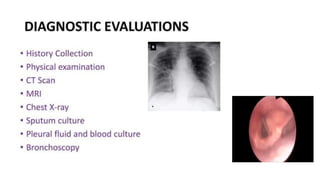
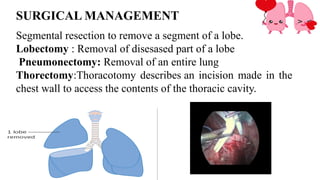
A lung abscess is a pus-filled cavity in the lung caused by a microbial infection, leading to symptoms like a persistent cough with foul-smelling sputum, fever, chest pain, and weight loss. Diagnosis is typically made with a chest X-ray, and treatment involves long courses of antibiotics, though sometimes drainage via a tube or surgical removal is necessary.
Causes
Aspiration: This is the most common cause, often occurring during a period of unconsciousness from anesthesia, sedation, or injury.
Underlying lung conditions: Diseases like bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis, or lung contusions can predispose individuals to developing a lung abscess.
Bacterial infections: The most common organisms are anaerobes and mixed anaerobic and aerobic bacteria.
Immune deficiencies: Conditions that compromise the immune system can increase the risk of a lung abscess.
Other conditions: Endobronchial obstructing lung cancer can also lead to a lung abscess.
Symptoms
Fever and chills
Persistent cough, often producing foul-smelling or blood-streaked sputum
Chest pain
Fatigue and weight loss
Night sweats