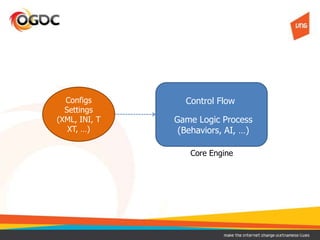
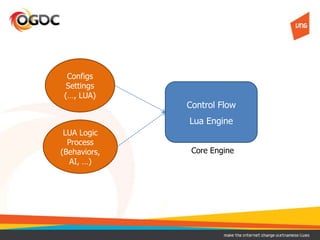
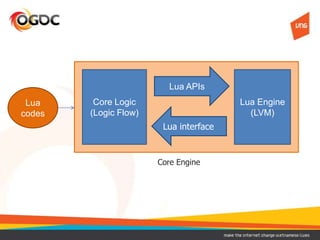
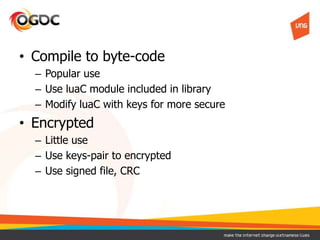
This document discusses using Lua in games. It provides an overview of Lua, including its benefits like being lightweight, portable, and easy to embed. It describes common models for integrating Lua into a game's core engine, including using Lua for config files, game logic, and controlling the core engine flow. It also discusses approaches for securing Lua code, such as compiling it to bytecode or encrypting it. Finally, it notes some disadvantages of Lua like low-level C APIs and difficulties debugging and reloading code at runtime.