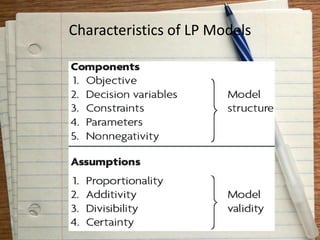
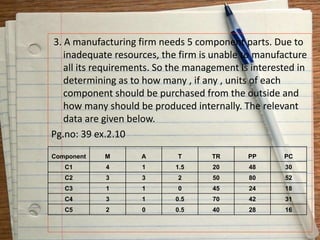
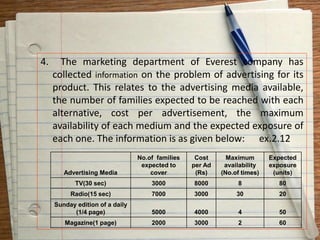
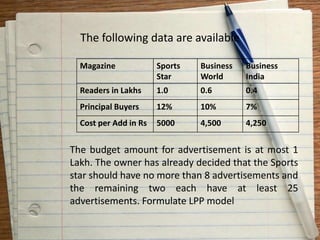
This document provides an introduction to operations research. It defines operations research as a scientific approach to decision making that seeks to determine how best to operate a system under conditions of allocating scarce resources. The document discusses the origin and applications of operations research. It also outlines some common operations research techniques like linear programming, transportation problems, assignment problems, and PERT-CPM. Finally, it provides definitions of operations research from different authors and discusses the scope and methodology of operations research.