LOWER RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.pptx upper respiratory tract, Respiratory system,Anatomy& Physiology
- 2. TRACHEA POSITION It is also called windpipe. It starts after the larynx and ends bronchi. It is a tubular passageway. Its length is 12 cm and diameter is 2.5 cm. The tube is kept patent because of the presence of C-shaped cartilaginous 'rings' in its wall. The cartilages are not present on posterior surface. This part is being made up of mus cles and fibrous tissues.
- 3. Structures Associated with the Trachea Superiorly : The larynx Inferiorly : The right and left bronchi. Anteriorly : Isthmus of the thyroid gland covering the 2nd and 3rd ring. Inferior thyroid veins below the isthmus. Posteriorly : Oesophagus, recurrent laryngeal nerve in the tracheo oesophageal groove. Laterally : Lobes of the thyroid gland.
- 4. Structure of Trachea : • The trachea is composed of C- shaped rings. • These rings are incomplete. • These rings are 16 to 20 in number, lying one above the other. • It is made up of hyaline cartilage.
- 5. cont.. The trachea consists of four layers from inward to outward as follows : • Mucosa : It is the inner most layer. The mucosa layer of trachea consists of epithelial layer of tissue. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium. This layer consists of goblet cells, which secrete the mucus. It provides protection against dust.
- 6. cont.. Submucosa : The submucosa consists of areolar connective tissue. It contains seromucus glands and their ducts. It contains the blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves. Hyaline cartilage : It is the third layer from inward to outward. This layer consists of fibrous and elastic tissues. It encloses the cartilage. It is C- shaped. It is arranged horizontally on one another.
- 7. cont.. Adventitia : It consists of areolar connective tissues. It joins the trachea to surrounding tissues.
- 8. Blood and Nerve Supply, Lymph Drainage : The Arterial Blood Supply : It is supplied by branches from the inferior thyroid arteries. Its veins drain into the left brachiocephalic vein. The Nerve Supply : Parasympathetic nerves (from the vagus) are sensory and secretomotor to the mucous membrane. It is motor to the trachealis muscle. Sympathetic nerves are vasomotor. They are supplied by the sympathetic ganglia.
- 9. cont.. The Nerve Supply : Parasympathetic nerves (from the vagus) are sensory and secretomotor to the mucous membrane. It is motor to the trachealis muscle. Sympathetic nerves are vasomotor. They are supplied by the sympathetic ganglia.
- 10. cont.. Lymph : There is an internal ridge, where the trachea divides into right and left bronchi, called the carina. Lymph from the respiratory passage passes through lymph nodes. These lymph nodes are present round the trachea and in the carina.
- 11. Functions of Trachea : The trachea has many functions, that are explained ahead: Cough Reflex : • There are nerve endings present in the larynx, trachea and bronchi. • These nerve endings are very sensitive to irritation. • When there is any irritating substance in the contact of larynx, trachea or bronchi, the message is conducted by the vagus nerves to the respiratory centre in the brain stem. • The motor response will result in deep breathing. • The glottis gets closed. • The abdominal and respiratory muscles then contract. • The air is released under pressure. • It will expel the mucus and foreign material outside the mouth.
- 12. cont.. Mucocillary Escalator : • The inner layer of the trachea larynx is lined with ciliated columnar epithelial cells. • The cilia is hair like projection. • The cilia provides the wave like movement. • It helps in propelling the contents i.e. dust towards larynx, where it is swallowed or expectorated.
- 13. cont.. Support and Patency : The trachea consists of cartilage and elastic tissues. It provides the trachea strength and rigidity. So, it prevents the kinking and obstruction of the airway, as the head and neck move. Cartilages are absent on posterior side. So, trachea can dilate and constrict on posterior side, during nerve stimulation and when food enters the oesophagus. The cartilage present in trachea prevents the collapse of trachea.
- 14. cont.. Warming, Humidifying and Filtering of Air : Trachea is lined with mucus membranes. This humidifies the air. It starts from the nose. Any dust particle, passing through trachea, irritates the trachea. It comes out with cough reflex. When the air enters the trachea it is present almost at body temperature.
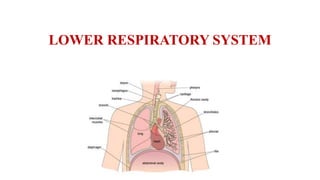
- 15. LUNGS Position and Associated Structures :- • The lungs are cone shaped organs. • They are present in the thoracic cavity. • They are separated by the heart and mediastinum. • The lungs are spongy in texture and are brown or grey in colour (in young). • Lungs are divided into right and left lung. • The weight of right lung is about 625g. • The weight of left lung is 575g. • The right lung is more heavier than left.
- 16. Features of lung :- The features of the lungs are : • The apex is blunt. • It lies above the level of the first rib. • It rises into the root of neck. • It reaches an inch above the medial 1/3 of the clavical. • It is covered by the cervical pleura and by the suprapleural membrane. • It is grooved by the subclavian artery on the medial side and in front.
- 17. cont.. The base : It is the inferior portion of the lungs. It is concave. It fits over the convex area of the diaphragm. It separates the right lung from the right lobe of the liver, the fundus of the stomach and the spleen.
- 18. Cont.. The anterior border : • It is very thin. • It is shorter than the posterior border. • The anterior border of the left lung shows a wide cardiac notch below the level of the 4th costal cartilage. • The posterior is thick. • It extends from the level of the 7th cervical vertebra to the 10th thoracic vertebra.
- 19. cont.. • The inferior border separates the base from the costal and medial surfaces. • It is associated with the costal cartilage, the ribs and the intercostal muscles.
- 20. cont.. • The medial surface : • It is concave. • It is roughly triangular shaped area, called hilum, at the level of the 5th, 6th and 7th thoracic vertebrae. • From the hilum, bronchi, pulmonary blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves enter and exit.
- 21. cont.. • The mediastinum is the area between the lungs. • There are present heart, great vessels, trachea, right and left bronchi, oesophagus, lymph nodes, lymph vessels and nerves.
- 22. Organisation of The Lungs • The right lung is divided into three lobes superior, middle and inferior. • The left lung is divided into two lobes superior and inferior. • The lobes are separated by the fissures. • There are two fissures in right lung and one fissure in left lung.
- 23. Pleura and Pleural Cavity • The pleura is the outer covering of lungs. • It is made up of serous membrane. • It contains a small amount of serous fluid. • This covering forms the sac, which covers the lungs. • It forms two layers.
- 24. cont.. • One layer adheres to the lung and other layer to the wall of the thoracic cavity. • The inner layer is called visceral pleura. • The outer layer is called parietal pleura.
- 25. cont.. The visceral pleura : This layer is adherent to the lung. It covers the lobes as well as fissures. The parietal pleura : This is the outermost layer. This layer is adherent to the wall of the thoracic cavity, the internal surface of the ribs and the superior surface of the diaphragm.
- 26. cont.. The pleural cavity : • The visceral and parietal pleura are not attached with each other. • They form the cavity pleural cavity. • This cavity is filled with fluid. • The fluid prevents the friction between two layers. • It also provides space for the expansion of lungs as the fluid acts as a lubricant. • If there is any injury to the pleura, the lungs collapse, due to their property of elastic recoil.
- 27. Interior of the Lungs • The lungs are composed of bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, connective tissues, blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves. • The lungs are made up of lobes. • The right lung consists of three lobes. • The left lung consists of two lobes.
- 28. Pulmonary Blood Supply: • The pulmonary trunk carries the deoxygenated blood. • This trunk is divided into right pulmonary artery and left pulmonary artery. • Both of these arteries carry deoxygenated blood. • From these arteries the blood reaches into the right and left unt of lung equally.
- 29. cont.. • Within the lungs pulmonary artery is divided into many branches which eventually end in a dense capillary network. • This network is present around the alveoli.
- 30. cont.. • The walls of alveoli and capillaries are made up of epithelial tissue. • These are single layer cells. • In this, the exchange of gases takes place through the alveoli. • The exchange of blood is through capillaries. • The blood is thus oxygenated. • These fine capillaries join to form the two pulmonary veins.
- 31. cont.. • It pours the blood into the heart. • It drains the blood into left atrium. • The small blood vessels and capillaries in the lungs consist of connec tive tissues.
- 32. BRONCHI AND BRONCHIOLES The trachea divides into two bronchi. It is called primary bronchi. The right bronchus is slightly wider than left. It is because, it lodges the foreign material that enters in the right bronchi. They are present at the level of 5th thoracic vertebra. There are two types of bronchi : Right Bronchus Left Bronchus
- 33. Right Bronchus : • The Right Bronchus: • This is wider, shorter and more vertical than the left bronchus. • When any foreign body enters, it obstructs the bronchus. • It is approximately 2.5 cm long. • It contains incomplete rings of cartilage. • It is lined by pseudostratified ciliated colum- nar epithelium. • The right bronchus is divided into three branches, one to each lobe. • Each branch is further subdivided into small branches.
- 34. Left Bronchus : • This is narrower than the right bronchus. • This is about 5 cm. • It is divided into two branches, one to each lobe. • It also consists of pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium. • The ring of cartilage is incomplete.
- 35. Structure : • The bronchi are composed of the same tissues as the trachea. • Each primary bronchus enters the lung on its respective side. • It is divided into smaller branches bronchi. • The secondary bronchi divided into tertiary bronchi. • It is divided into alveolar ducts. • This terminates in alveoli. • Some 300 million alveoli are present in two lungs.
- 36. Blood and Nerve Supply : The Arterial Blood Supply : • The right and left bronchial arteries supply the blood to the walls of the bronchi and small air passages. • Bronchial veins return the venous blood. • From right side of bronchi, blood comes into azygos vein and from left side comes into the superior vein. The Nerve Supply : (Parasympathetic nerve supply) • It is sensory and secretomotor to the mucous membrane and motor to the trachealis muscle. • Sympathetic nerve supply to the thyroid arteries is vasomotor. • It helps in the bronchodilatation.
- 37. Respiratory Bronchioles and Alveoli Structure :- Distal to the terminal, the bronchioles consist of, respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts and alveoli (Tiny air sacs). The alveoli are the primary structures for gas exchange. The alveoli have very thin walls, so the gases as carbondioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2) can exchange. It consists of simple squamous epithelial cells present in the alveolar ducts and alveoli.
- 38. cont.. The barrier across which gases are exchanged between alveolar air and the blood is called the respiratory membrane. The surface of each membrane is coated with a fluid containing surfactant. Surfactant reduces the surface tension. Thus it helps each alveolus from collapsing, as air moves in and out during respiration. The surfactant prevents the alveoli from drying out.
- 39. Functions of Respiratory Bronchioles and Alveoli • Gas Exchange : In the alveoli, there is a network of capillaries which helps in the exchange of gases between air and blood. • Warming and Humidifying : The mucous layer provides the moist air. The capillary bed warms the air. • Removal of Dust : A protective layer of mucus is present. The foreign bodies stick to it causing irritation of mucous membrane, resulting in cough or sneezing. In this way, the foreign body is thrown out. • Defence Against Microbes : The alveoli is composed of connective tissues. They include the lymphocytes and plasma cells. These cells synthesise and secrete antibodies, which fight against the foreign bodies.