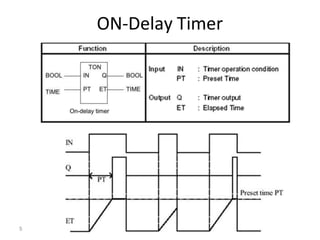
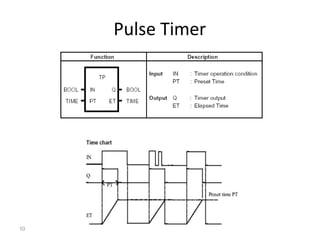
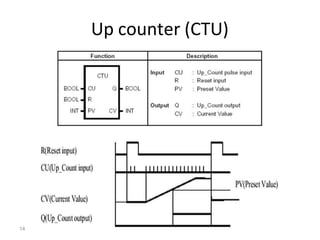
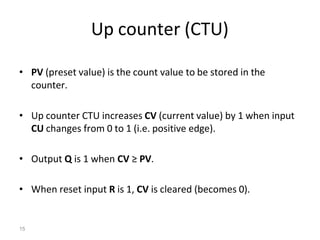
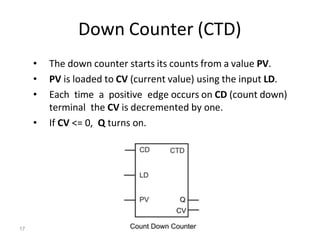
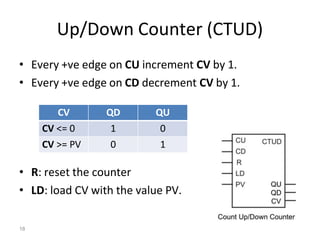
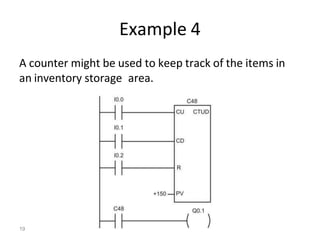
This document discusses timers and counters in PLC ladder programming. There are three basic types of timers: on-delay timers, off-delay timers, and pulse timers. On-delay timers turn on their output after a preset time interval after their input turns on. Off-delay timers turn off their output after a preset time interval after their input turns off. Pulse timers turn on their output for the preset time interval when their input turns on. Counters keep track of events and include up counters, down counters, and up-down counters. Up counters increment their value on each positive input edge until a preset value is reached. Down counters decrement their value on each positive input edge until reaching zero.