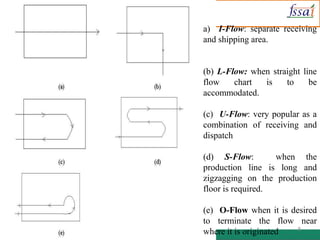
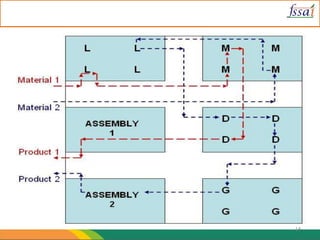
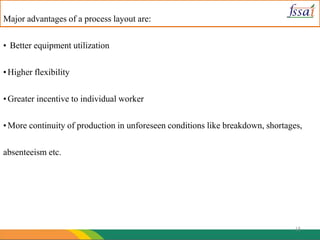
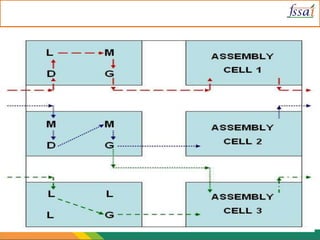
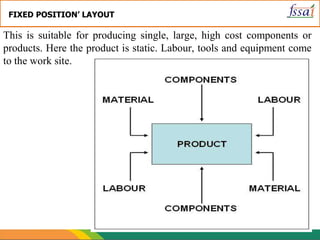
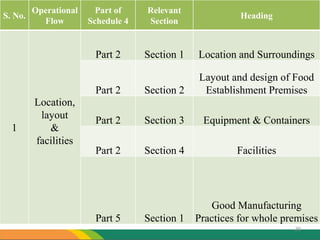
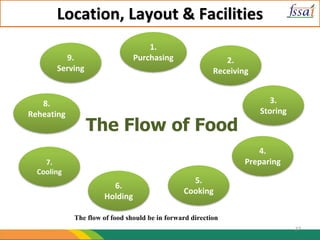
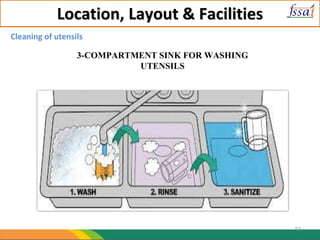
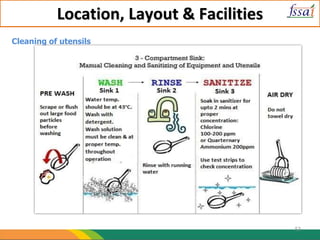
The document discusses various aspects of food processing plant layout including location, facilities, equipment, and flow patterns. Some key points:
1. The layout should facilitate one-way material flow without cross-contamination. Floors, walls, and ceilings must be smooth, impervious, and easy to clean.
2. Equipment and containers must be corrosion-free, easy to clean, and used only for intended purposes. Cleaning and waste disposal systems should also be provided.
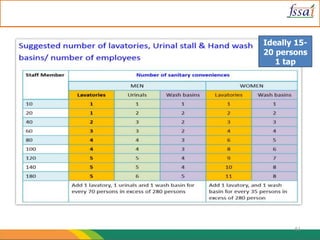
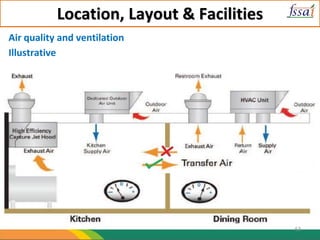
3. Facilities like potable water, handwashing stations, lighting, ventilation, and separate changing/eating areas are required to maintain hygiene.