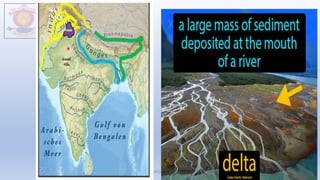
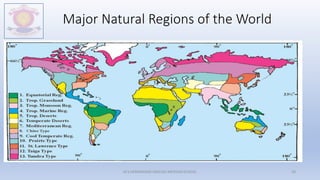
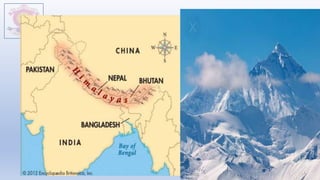
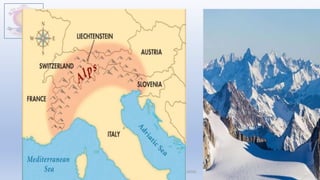
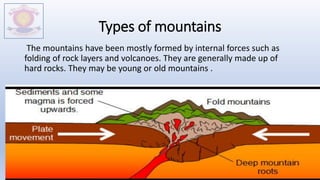
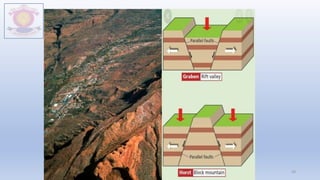
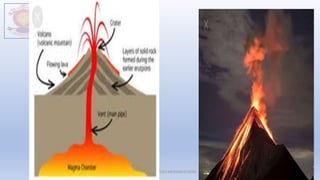
The document discusses different types of major landforms including mountains, plateaus, plains, deserts, and islands. It describes the key characteristics of each landform type and provides examples. Mountains are formed by folding of rock layers and volcanoes, and include young mountains with steep slopes like the Himalayas and older mountains with more rounded peaks. Plateaus are flat elevated lands with steep sides, and include intermontane, piedmont, and continental plateaus. Plains are extensive flat or undulating lands formed by deposition, erosion, or uplift, and support agriculture. Deserts are very dry areas with little rainfall, and islands are areas of land surrounded by water.

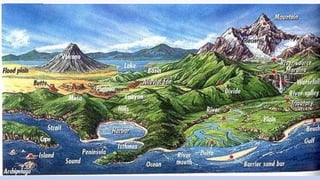

















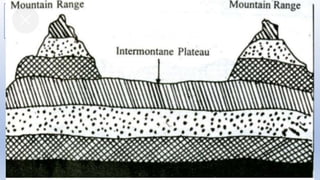
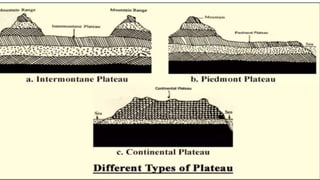

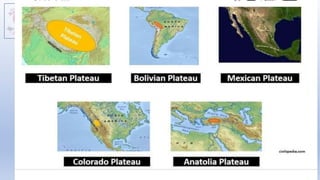
![Piedmont Plateaus
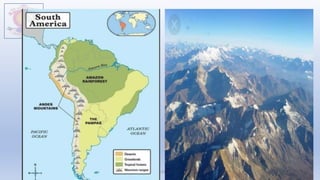
• Piedmont Plateaus have mountains on one side and
plains or ocean on the other, e.g. Patagonian Plateau
[South America]
M.V.HERWADKAR ENGLISH MEDIUM SCHOOL 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-220825092803-c3907b87/85/L-NO-7-Major-landforms-6TH-pptx-30-320.jpg)