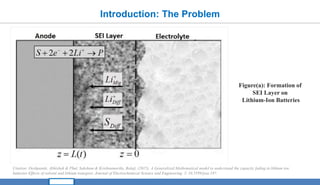
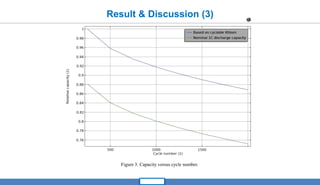
The document presents a mathematical modeling and analysis of capacity fade in lithium-ion batteries, focusing on the degradation processes during cycling periods. Key findings highlight the influence of solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation on capacity fade, providing predictive insights for diverse applications. The research aims to contribute to sustainable energy transitions by enhancing the longevity and effectiveness of lithium-ion batteries.