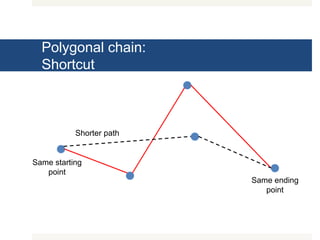
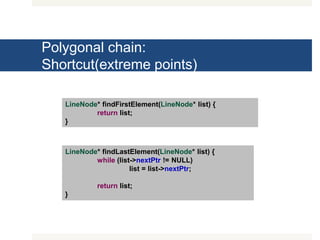
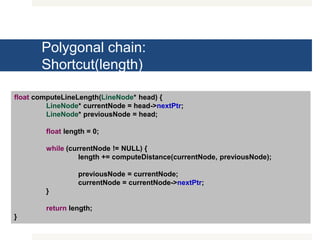
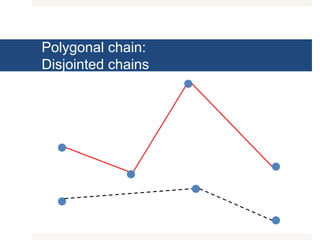
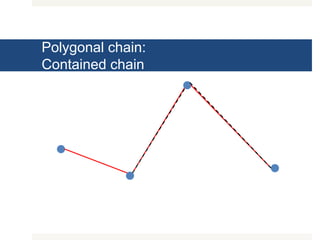
The document outlines various exercises and functions related to linked lists and polygonal chains, covering operations such as summing elements, finding maximum and minimum values, reversing a list, and identifying peaks. It also describes functions for manipulating polygonal chains, including checking for shortcuts, disjointedness, and containment relations. Additionally, it introduces further exercises regarding extensions, concatenation, and tortuosity of polygonal chains.