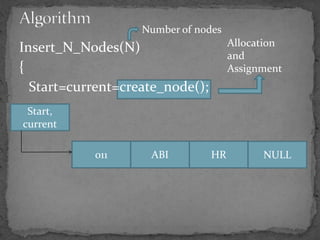
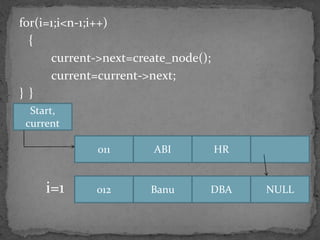
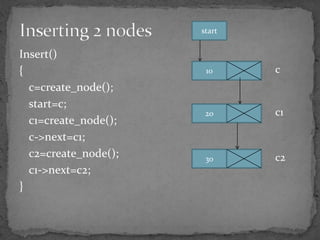
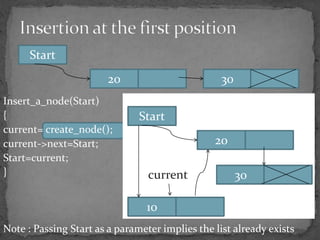
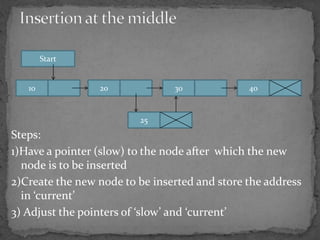
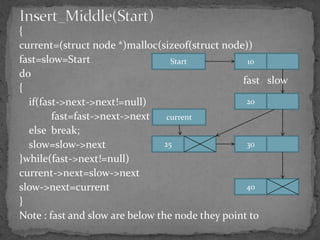
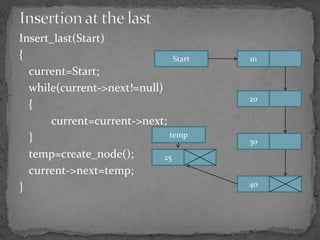
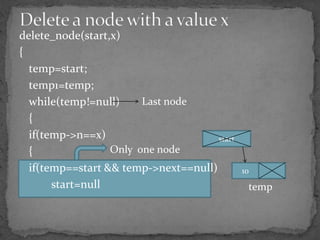
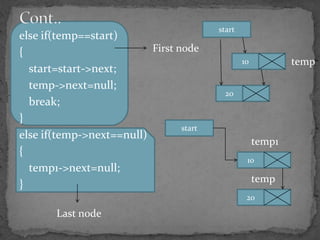
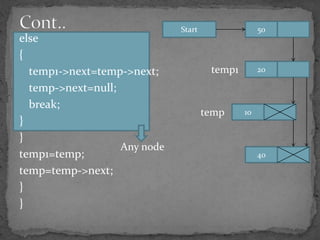
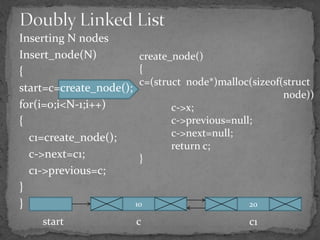
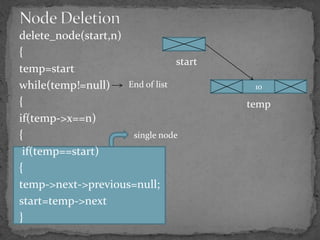
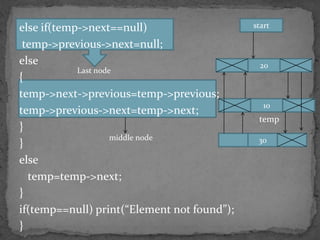
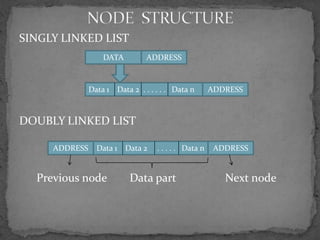
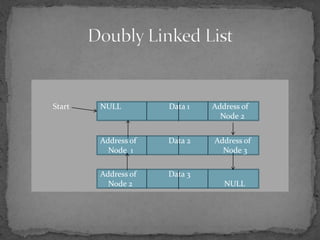
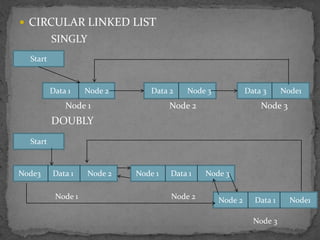
The document discusses different types of linked lists including singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists. It also covers operations for linked lists such as inserting nodes, deleting nodes, and finding the middle node. Examples are provided for implementing linked list operations using C code.


![struct node
{
int x;
x c[10] next
char c[10];
struct node *next;
}*current;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkedlist-withoutanimation-130327234113-phpapp02/85/Linked-list-without-animation-6-320.jpg)
![create_node()
{
current=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
current->x=10; current->c=“try”; current->next=null;
return current;
}
Allocation x c[10] next
Assignment 10 try NULL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkedlist-withoutanimation-130327234113-phpapp02/85/Linked-list-without-animation-7-320.jpg)
![Create a linked list for maintaining the employee details
such as Ename,Eid,Edesig.
Steps:
1)Identify the node structure struct node
{
2)Allocate space for the node
int Eid;
3)Insert the node in the list char Ename[10],Edesig[10];
struct node *next;
} *current;
EID EName EDesig next](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkedlist-withoutanimation-130327234113-phpapp02/85/Linked-list-without-animation-8-320.jpg)