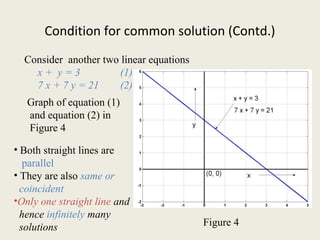
This document discusses linear equations in two variables. It begins by presenting the general form of a linear equation as ax + by + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers. It then explains that a single linear equation represents a straight line and can have infinitely many solution pairs (x,y). The document also discusses how two linear equations can have a unique solution if their lines intersect, no solution if the lines are parallel, or infinitely many solutions if the lines are coincident. Finally, it presents different algebraic methods for solving systems of two linear equations, including substitution, elimination of coefficients, and cross-multiplication.










![Solution of System of Linear Equations by Cross
Multiplication
Consider two linear equations
a1 x + b1y + c1 = 0, a1≠ 0, b1≠ 0 (1)
a2 x + b2 y + c2 = 0, a2 ≠ 0, b2 ≠ 0 (2)
Eliminate y by substitution. From (1) we get
y = – (1/ b1 )(c1 + a1 x) b1 ≠ 0 (given)
Substitute y in (2), we get
a2 x + b2 [– (1/ b1 )(c1 + a1 x) ] + c2 = 0
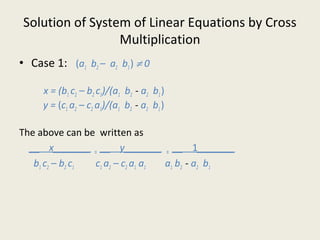
or (a1 b2 - a2 b1 ) x = b1 c2 - b2 c1 (3)
Similarly by eliminating x, we get
(a1 b2 - a2 b1 ) y = c1 a2 - c2 a1 (4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linearequns-classx-180912070018-220927090744-49256ae8/85/linearequns-classx-180912070018-pdf-13-320.jpg)