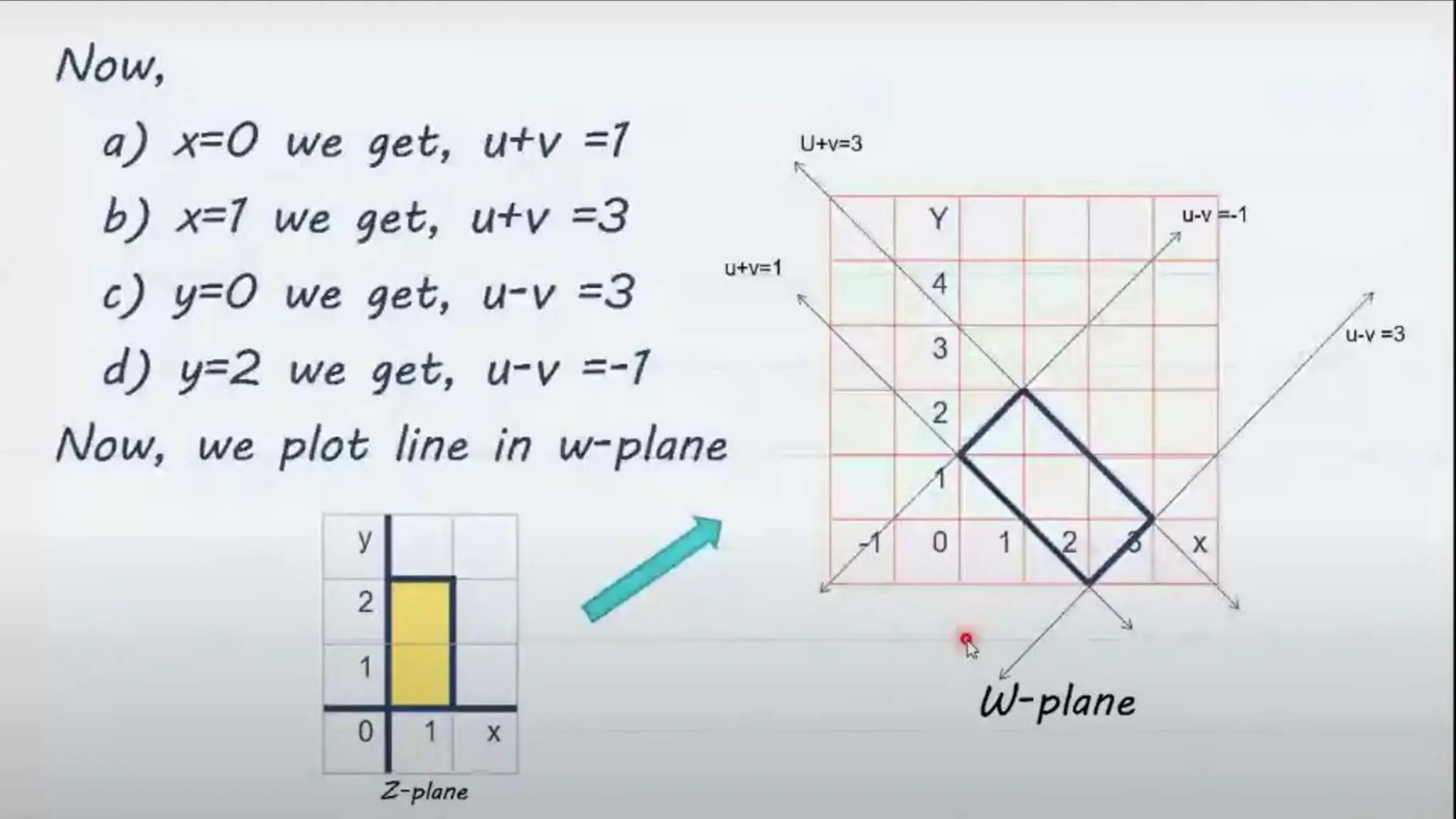
This document discusses linear and bilinear mappings. It begins by defining mapping as the process of associating elements between sets. Linear mapping is described as a mathematical function that transforms data using a matrix, having properties like linearity and additivity. It provides examples of linear mapping applications in areas like engineering, data analysis, and physics. Bilinear mapping is then introduced as a mapping that combines elements from two vector spaces to return a scalar value. The document notes differences between linear and bilinear mappings and provides concluding remarks about their respective applications and importance.