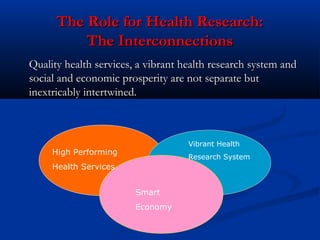
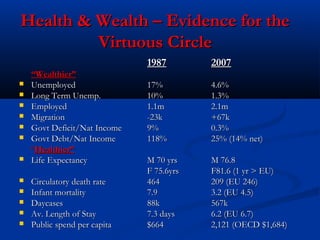
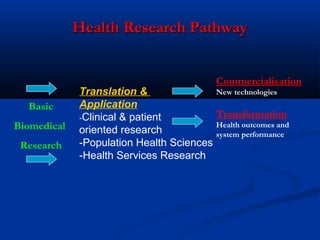
This document summarizes a presentation on aligning health innovation with service needs and economic opportunity. It discusses how health services have become more complex, knowledge-intensive, and expensive but have also added years and life to years. Health service transformation is driven by reducing budgets, demand for access and quality, technology advances, and chronic disease burden. The preferred model focuses on prevention, chronic illness programs, primary care teams, and centralizing specialist services. It is argued that high-performing health services, vibrant research, and a smart economy are intertwined. Progress is reported on implementing Ireland's Action Plan for Health Research, including developing clinical research facilities and a national biobanking solution.