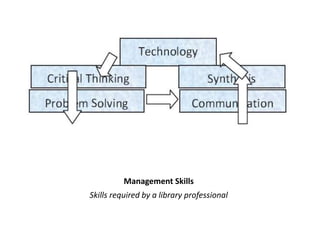
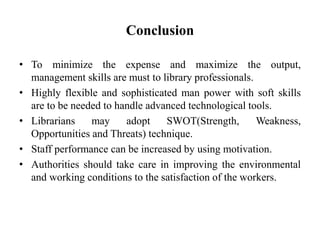
This document discusses library and information management. It begins by noting how technology has impacted libraries and their operations. The objectives of the study are then outlined, including examining the need for management skills among library professionals. Several management skills that are important for library professionals are also listed, such as technical, communication, and problem solving skills. The roles of librarians and different types of library staff are then described. Finally, the conclusion emphasizes that management skills are necessary for library professionals to minimize costs and maximize output in today's technological environment.