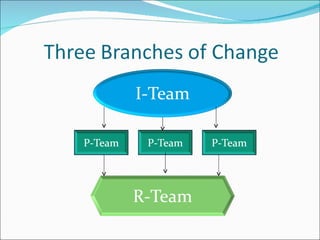
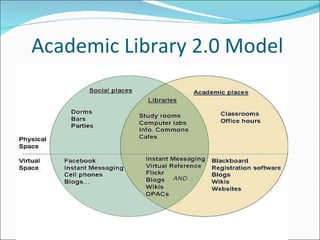
Library 2.0 aims to put users at the center by breaking down barriers and encouraging collaboration and new content creation. It emphasizes constant evaluation and purposeful change driven by user feedback, practicing constant learning, and blending social and academic functions. Access services staff have an essential role to play in evaluating services, implementing changes, and helping the library adopt a Library 2.0 model.