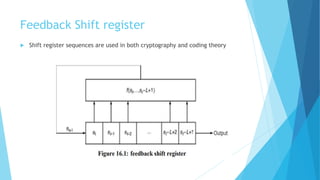
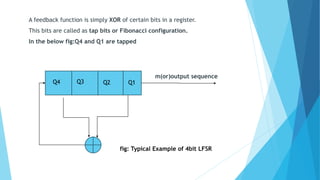
This document summarizes a presentation about linear feedback shift registers (LFSRs). It defines an LFSR as a type of feedback shift register that uses a linear feedback function, typically an XOR of certain bits in the register. An LFSR can generate long pseudo-random sequences of 1s and 0s before repeating, with the period of an n-bit LFSR being 2n - 1. The feedback function is applied after each shift to determine the next bit. LFSRs are commonly used in cryptography due to their ability to generate random-looking sequences. The document provides an example of a 4-bit LFSR and discusses the use of primitive polynomials to ensure maximum periods. It also lists some applications of LFSRs