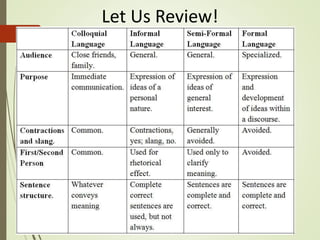
This document discusses the varying levels of formality in writing, emphasizing the importance of understanding audience and purpose for effective communication. It categorizes language into colloquial, informal, semi-formal, and formal styles, detailing characteristics and appropriate contexts for each. The lesson encourages consideration of diction to achieve clarity and appropriateness in various writing situations.