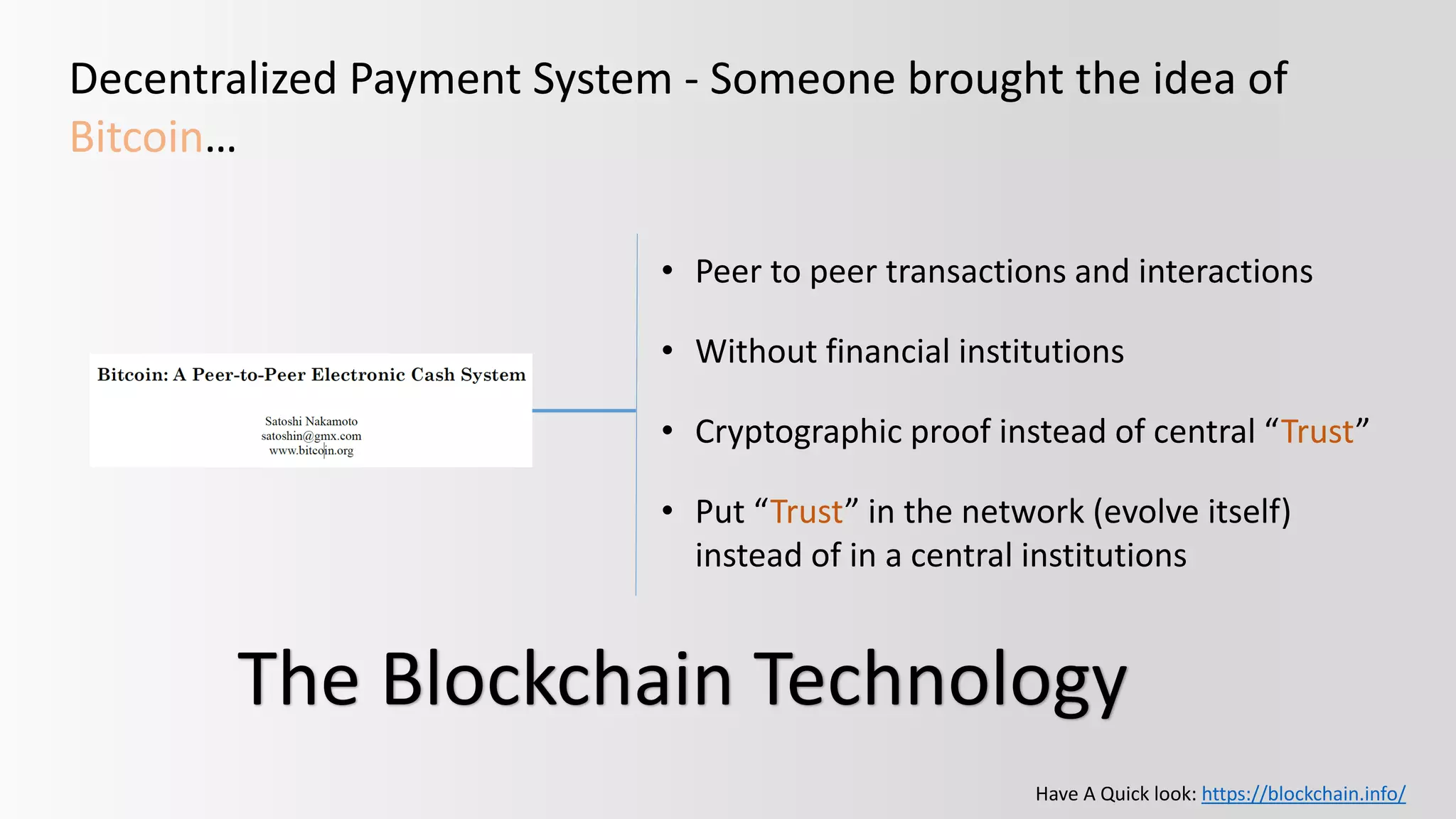
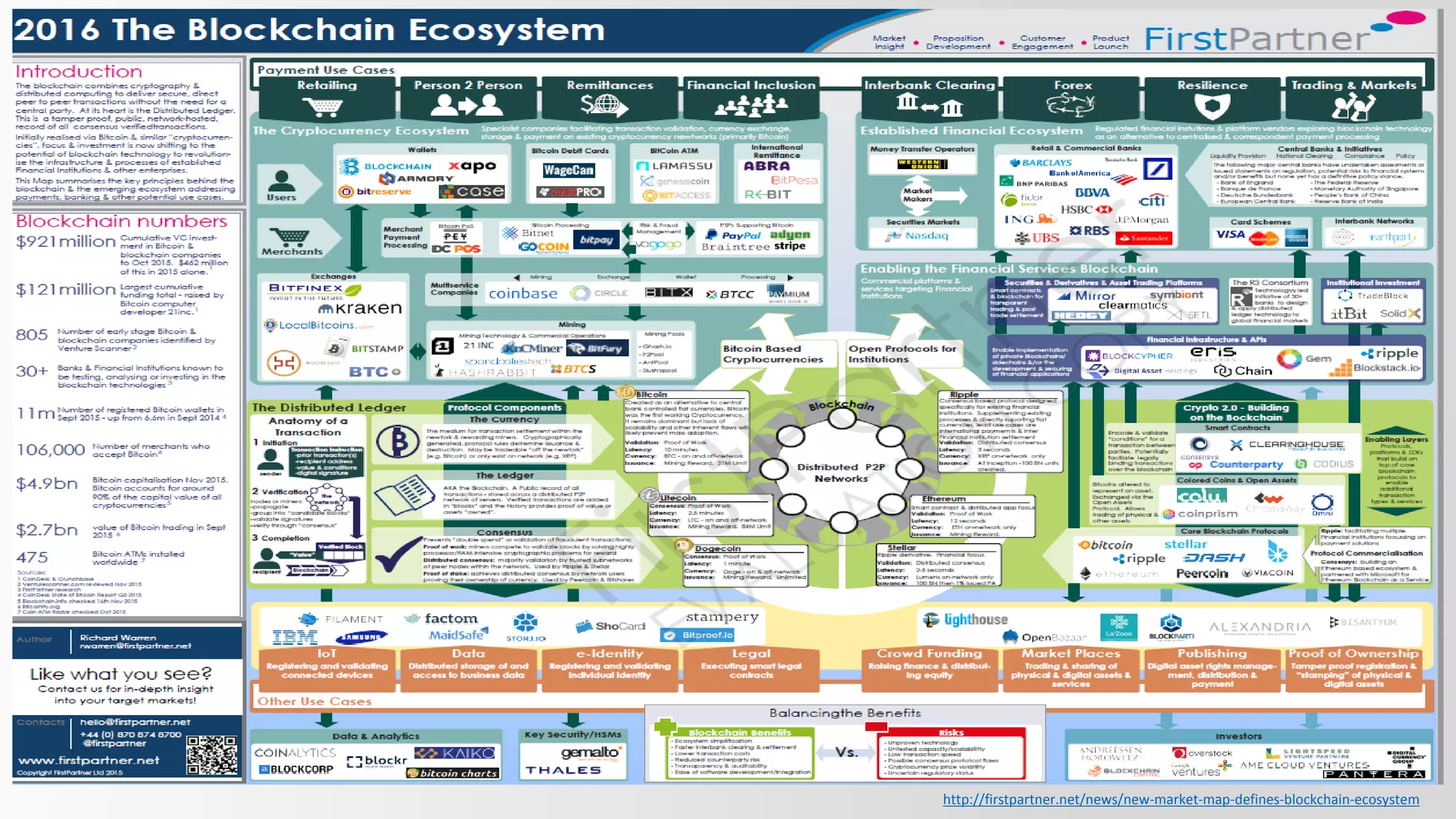
The document discusses the concept of trust in various aspects of life, emphasizing the reliance on trusted third parties such as banks and governments, and the consequences of trust breaches. It introduces decentralized payment systems like Bitcoin and the role of blockchain technology in establishing trust without central authorities, promoting peer-to-peer transactions. Additionally, it outlines the evolution of blockchain technology from simple currency to smart contracts and decentralized applications, highlighting its potential across multiple industries.